TL;DR: Atwood's law states that Any application that can be written in JavaScript, will eventually be written in JavaScript. In 2018, eleven years after this law was proposed, JavaScript is now the most popular language in the world. In this tutorial, I'll show you how to deploy your JavaScript applications to different cloud platforms such as Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Netlify, and others. This article is not about performance.
The Client-Server Architecture
Modern applications employ the client-server architecture. This architecture separates application software into two categories, clients and servers to better utilize available computing resources and share data processing loads. These categories are otherwise known as, front end, and back end. The client and server application can be hosted on the same machine but it's more efficient and effective when the client and server applications are hosted and executed on different machines connected via a network.
The client-server architecture aids efficiency by allowing the option of having different clients consume a server resource. These clients could be Single Page Applications (SPAs), mobile applications, or non-interactive clients such as CLIs or Daemons.
In recent times, most JavaScript applications are bundled and deployed as Single Page Applications running on Vanilla JS, Vue, React, Polymer, Angular, consuming and pushing data to a backend application running on Node. The front end/back end model of building software is common not only in the JavaScript community, but the developer community at large. And these applications are deployed to cloud servers.
Introduction to Cloud Server
Cloud servers are basically virtual servers that run within a cloud computing environment. There are various benefits to hosting and deploying your applications on the cloud. They are:
- Economically efficient.
- You have the freedom to modify the server software to your needs.
- Cloud servers scale very well.
- Stability and security.
In fact, many companies have moved their infrastructure to the cloud in order to reduce cost and complexity. It's a great option for small, mid-sized, and enterprise scale businesses. If you write a lot of tutorials and do POCs (Proof-of-concepts) like me, it's also a great choice for you!
A generic JavaScript application involves a:
Front end: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. A couple of CSS frameworks that can be used on the front end are:
Bootstrap: The most popular CSS framework in the world
- Bulma: A modern CSS framework based on Flexbox
Tailwind: A utility-first CSS framework for rapid UI development
A couple of JavaScript frameworks that can be used on the front end are:
Back end: JavaScript running on a Node.js server. Some frameworks that can be used on the back end are:
Express: Fast, unopinionated, minimalist web framework for Node.js.
- Hapi: Rich framework for building applications and services.
Koa: Next generation web framework for Node.js.
- Sails: Realtime MVC framework for Node.js.
Examples of Databases that can be used are:
Application To Deploy
In this tutorial, we'll be deploying this sample application, Meetups. The Architecture is not complex. It's composed of a back end and a front end.
The back end is comprised of the following:
- A MongoDB Database
- A Node.js web framework - Express
The front end is comprised of the following:
- Vue.js
- JavaScript front end framework.
- Twitter Bootstrap
- CSS framework for styling our app.
Application Key Requirements
In order to run Meetups, you need to have the following tools installed on your machine.
- Node.js: Navigate to the Node.js website and install the latest version on your machine. Ensure that
works via the terminal.npm - MongoDB: Navigate to the MongoDB website and install the MongoDB community server edition. If you are using a Mac, I'll recommend following this instruction. To avoid micromanaging from the terminal, I'll also recommend installing a MongoDB GUI, Robo 3T, formerly known as RoboMongo. You can then run
from the terminal to start up the MongoDB service on your machine.mongod
MongoDB works seamlessly with Node.js backends.
Next, let's cover how to deploy this sample JavaScript application. First, we'll hand over the database management to a cloud service. One great benefit of operating a remote database is having several apps pull data from the database service. In addition, you can optimize as much as possible because of the dedicated service your database runs on.
Database Deployment
There are several database cloud services that can manage your database effectively. For relational databases, we have some great services such as:
- Amazon RDS (SQL) / Amazon Aurora
- Microsoft Azure SQL
- Google Cloud SQL
- Elephant SQL
For NoSQL databases such as the database Meetups operates, we have some services such as:
mLab
mLab is a cloud platform that provides Database-as-a-service for MongoDB. The free version provides developers with 500MB storage. Let's go ahead and create a database for our app on mLab.
Make sure you follow these steps below:
- Create an account with mLab
- Go to the mLab Dashboard and click the "Create new" button.
- Choose a Cloud Provider amongst these three providers, Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure. For this tutorial, I chose Amazon Web Services.
- Select a Plan type amongst these plans: Sandbox, Shared, and Dedicated. For app prototyping, POCs, and demos, I recommend the Sandbox option which is free and has up to 0.5GB storage.
- Choose a region for the Cloud Provider you previously selected and click on "Continue". It's always recommended to choose a region closer to you or your target market.
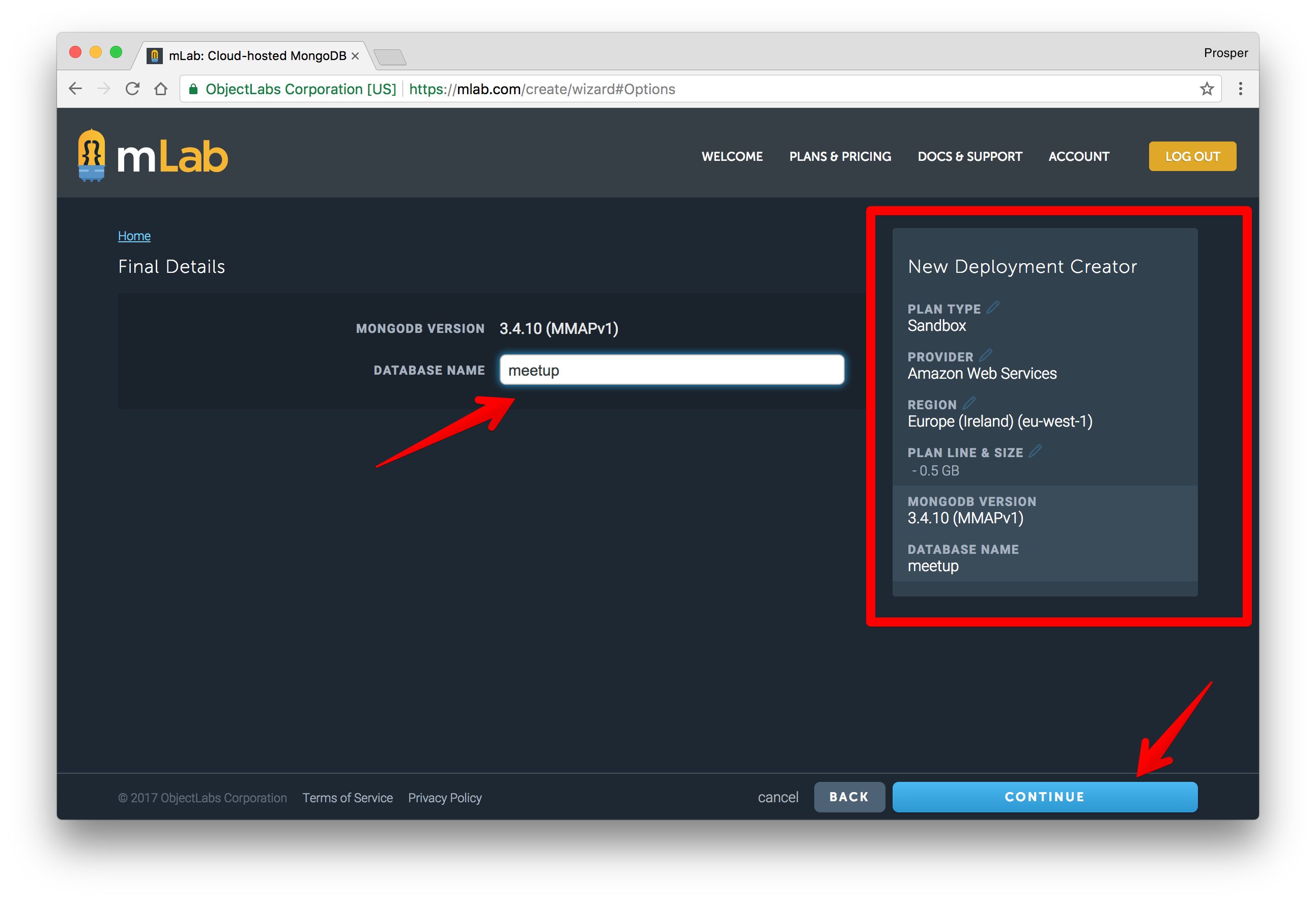
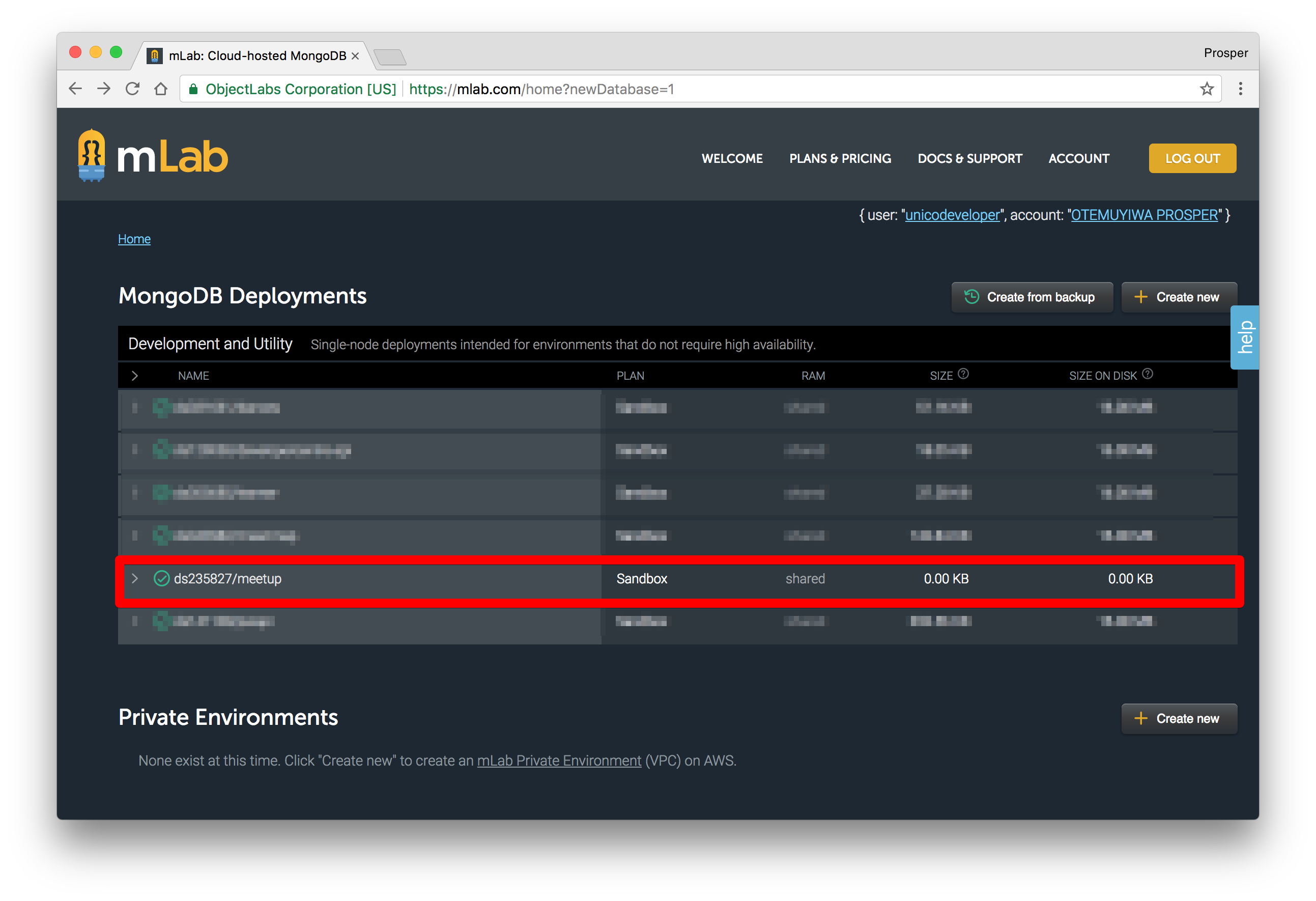
Choose a database name. I chose
.meetupClick "Continue". Once it has been created, you'll see the database on the dashboard like so:
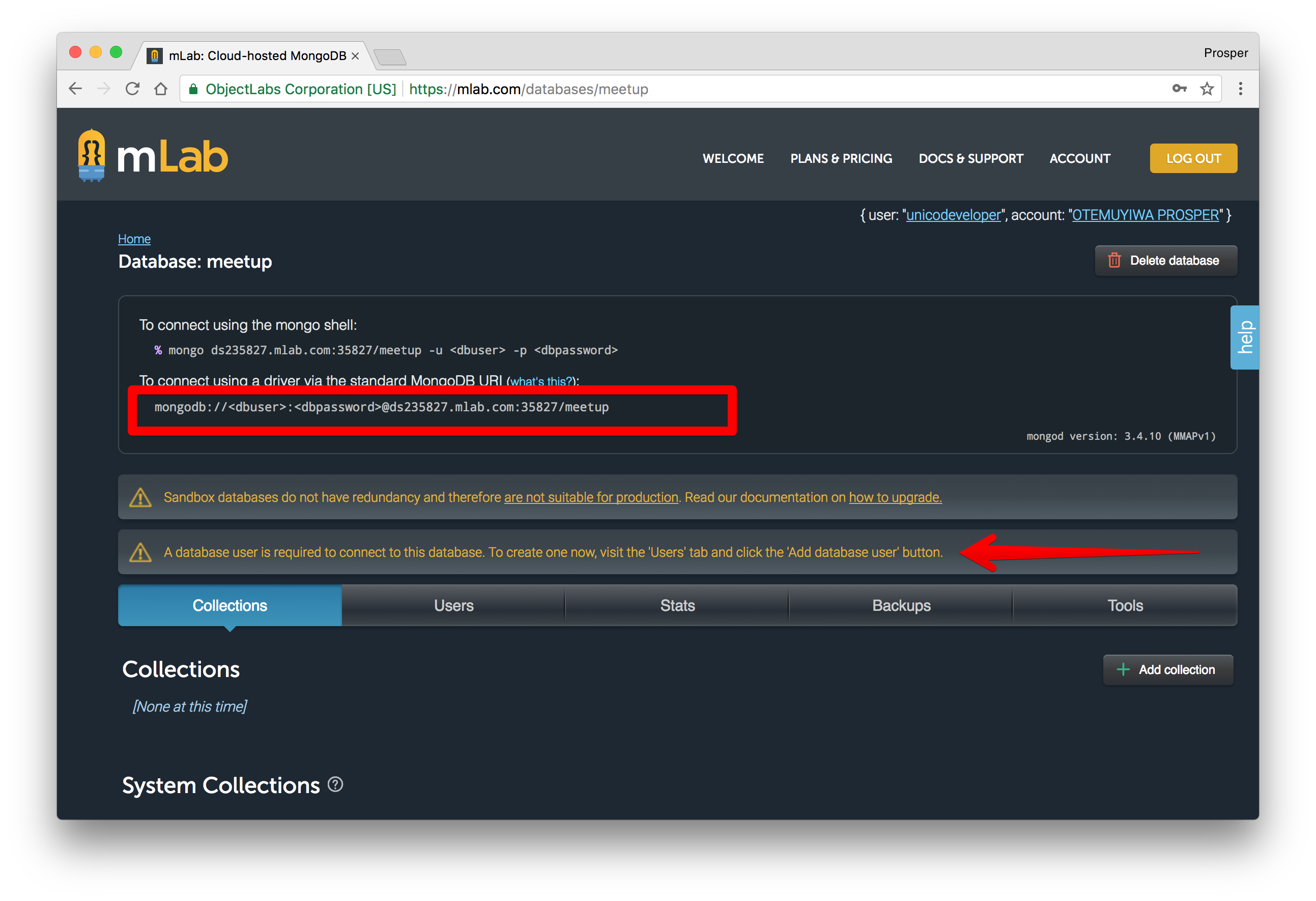
Click on the recently created database. An interface will be presented to you with a connection string like so:
This is the connection string:
mongodb://<dbuser>:<dbpassword>@ds235827.mlab.com:35827/meetup<dbuser><password>All I need to do is replace my local connection string with that of mLabs.
Note: In a real-world scenario, you should have a config file with the local and production connection strings. You can use
to determine whether the app is running locally or on production and assign the appropriate database connection string based on the environment.process.env
MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas is a cloud platform that also provides Database-as-a-Service for MongoDB. The free version provides developers with 512MB storage. Let's go ahead and create a database for our app on MongoDB Atlas.
Make sure you follow these steps below:
- Create an account with MongoDB Atlas
- A dialog box will be presented to you with a lot of form fields.
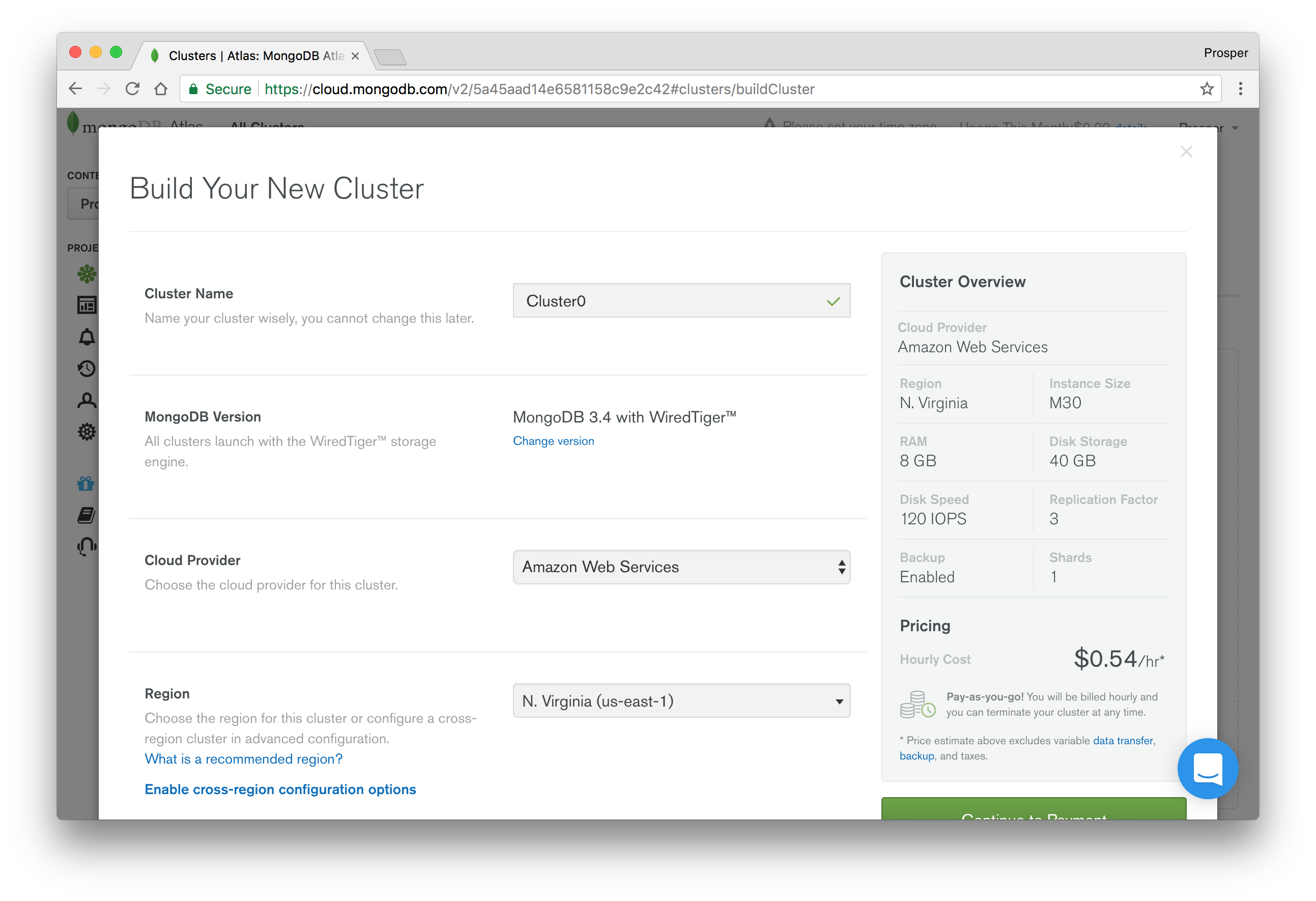
Choose a name for your cluster, a cloud provider, and region like so:
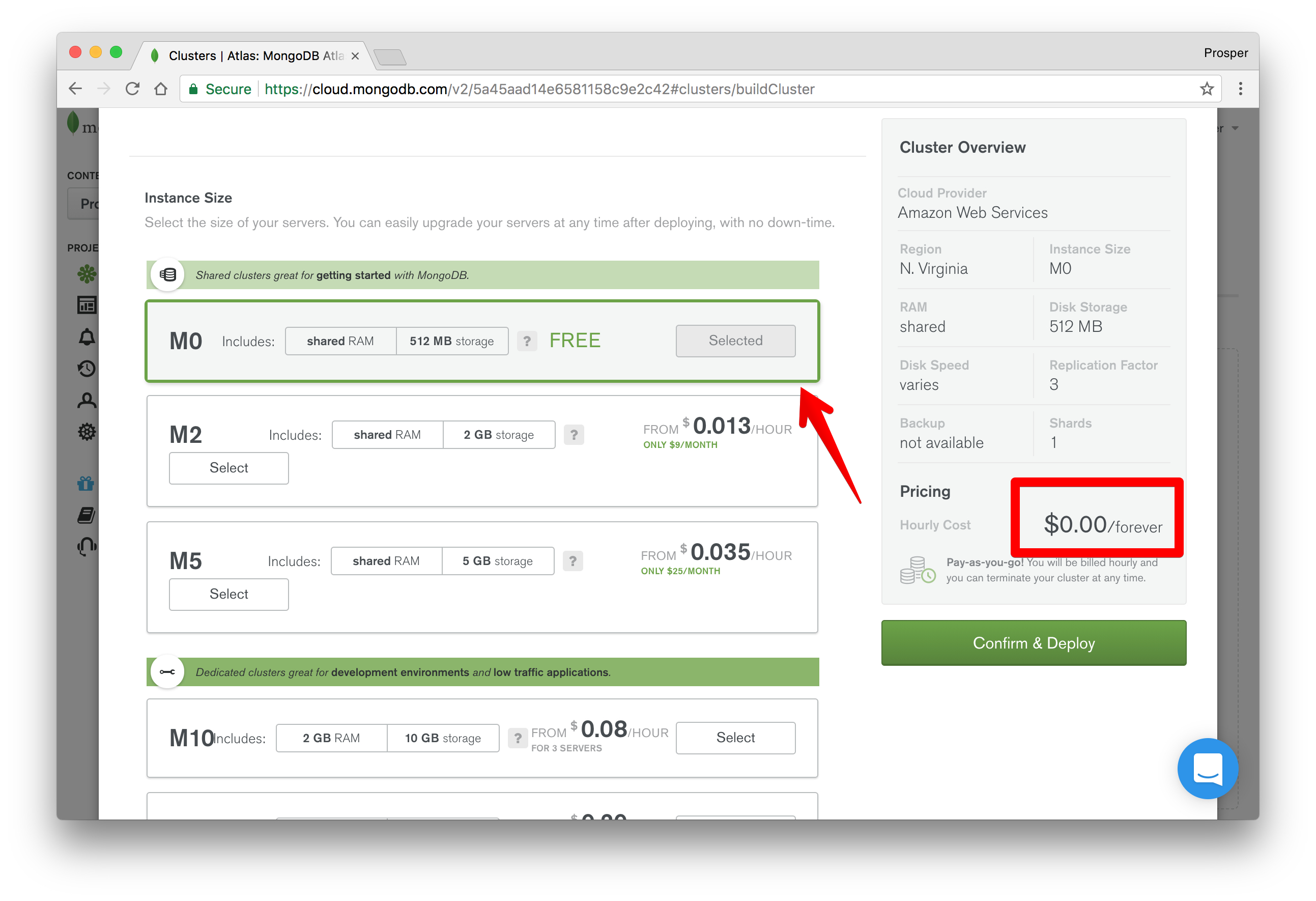
Scroll down a bit to Instance size. Here you can choose a plan for your app. I chose the free version for the purpose of this tutorial. The free version is also great for prototyping, POCs, and demos.
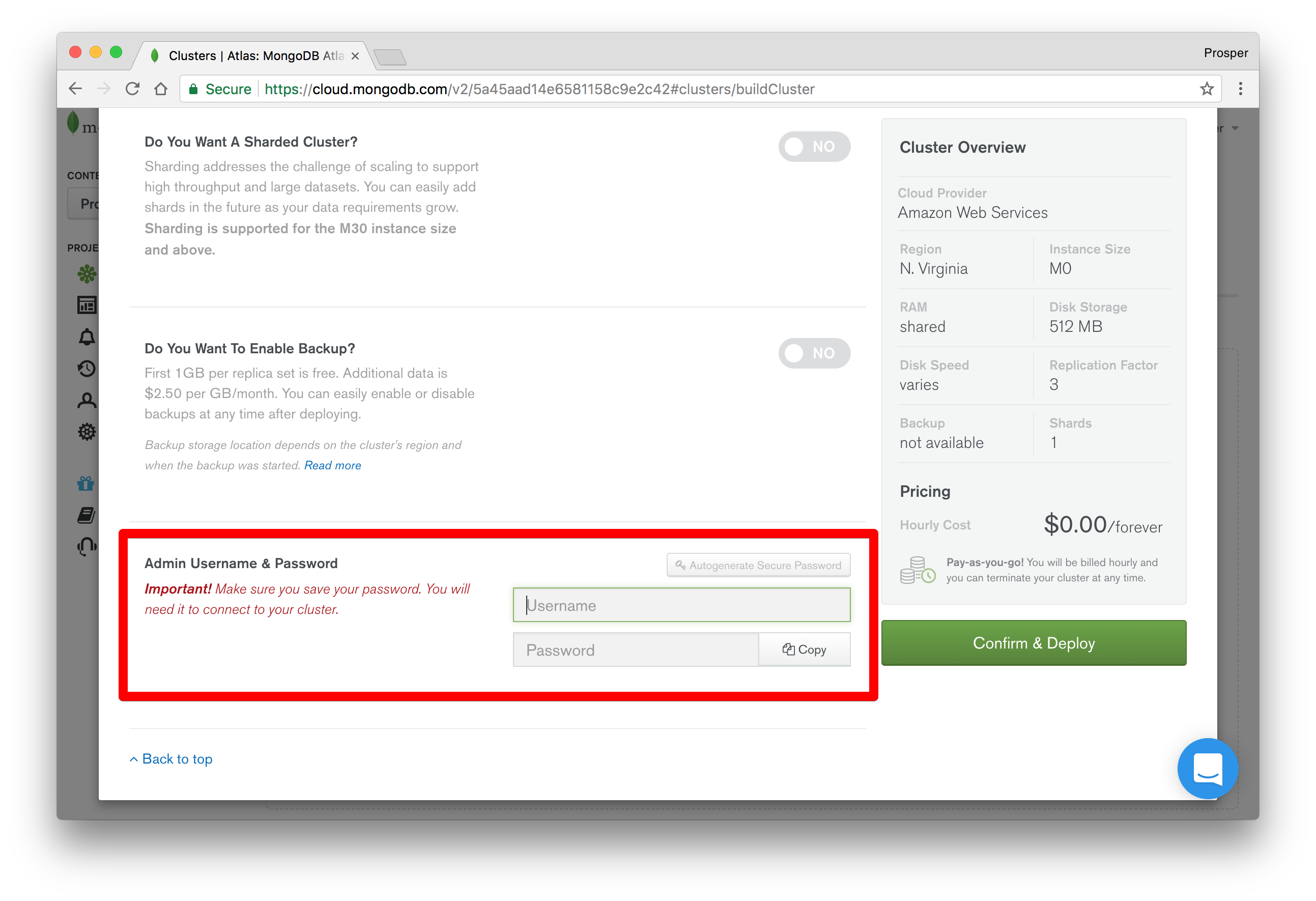
Scroll down and provide a username and password that your app will use to connect to your cluster.
- Click on Confirm and Deploy. Confirm that you are not a robot and your cluster will be created within seven to ten minutes. It's noteworthy to let you know that this is the longest time I've seen a service take to provision a fresh database cluster.
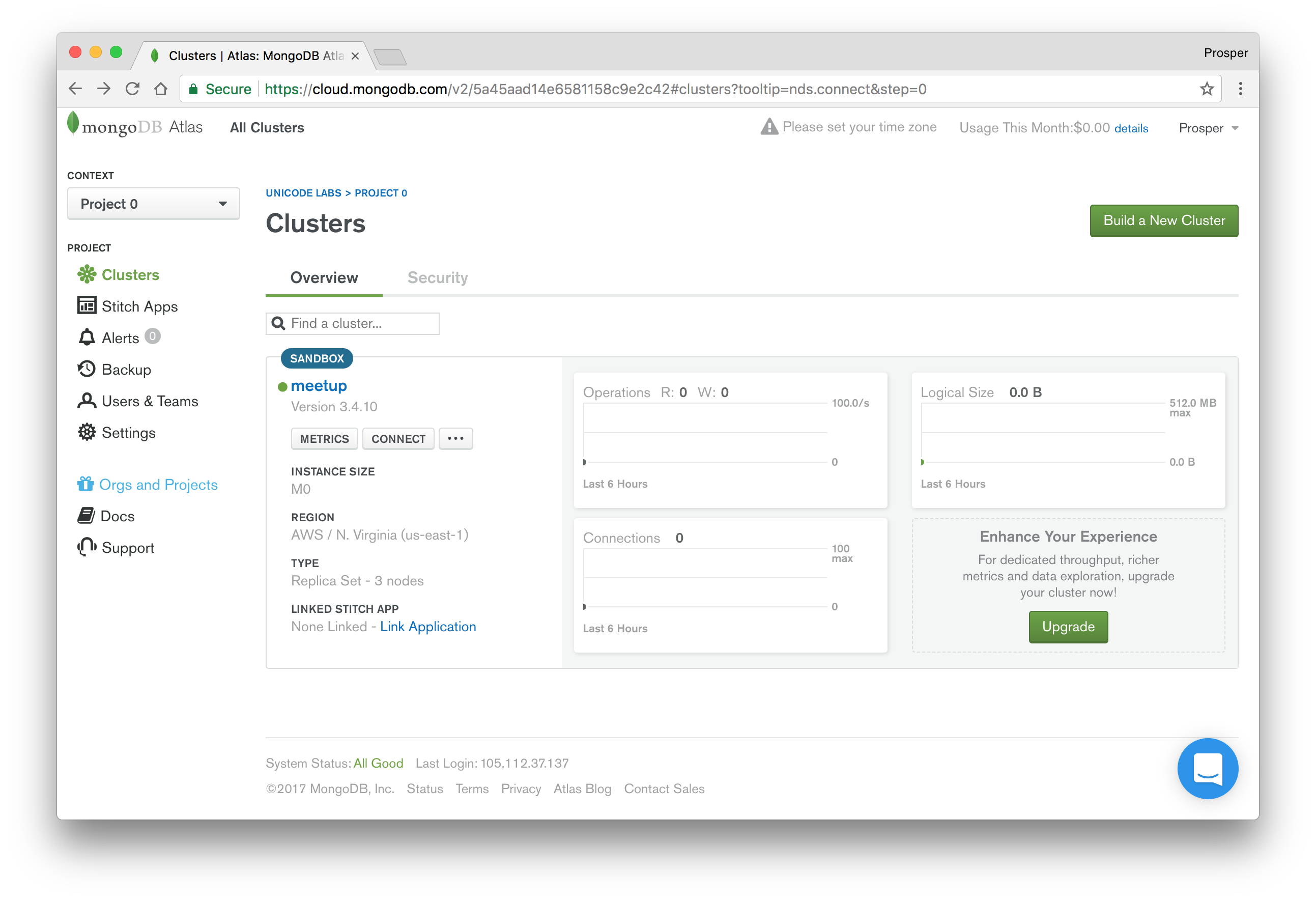
- Once it is done provisioning, your dashboard should look like so:
- The next step is to click the Connect button. You'll be asked to whitelist an IP address or you can simply allow access from anywhere. I particularly like this feature, for security reasons.
- Choose a connection method. I chose Connect Your Application because that's what is needed for our use case.
- Select the MongoDB driver appropriate for your use case and copy the respective URI connection string. Mine is
.mongodb://unicodeveloper:<PASSWORD>@meetup-shard-00-00-hjyfh.mongodb.net:27017,meetup-shard-00-01-hjyfh.mongodb.net:27017,meetup-shard-00-02-hjyfh.mongodb.net:27017/test?ssl=true&replicaSet=meetup-shard-0&authSource=admin
Note: Replace
with the name of your database, else all your data will be stored intestdatabase.test
Amazon DynamoDB
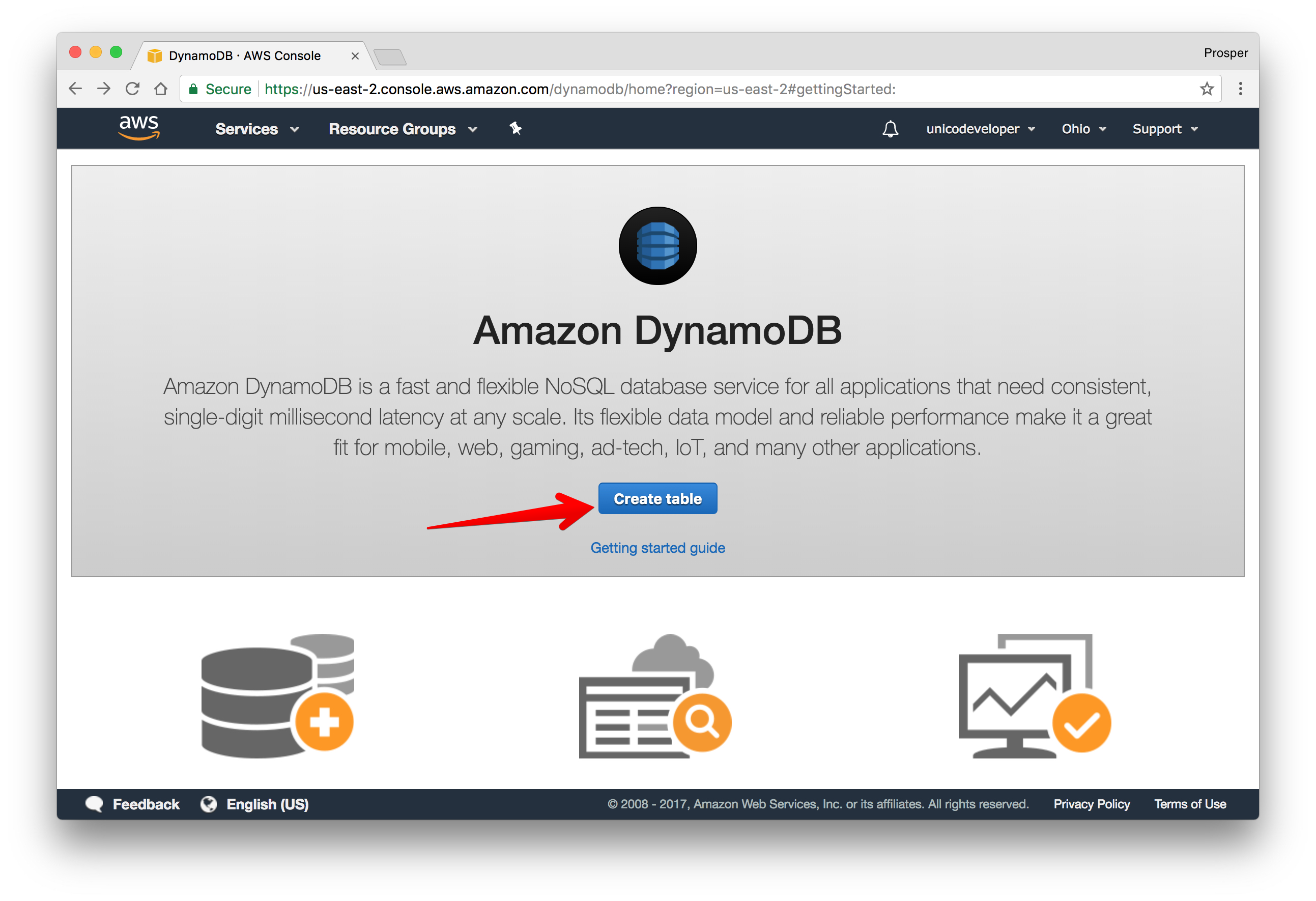
Amazon DynamoDB is a cloud platform that provides a fast and flexible NoSQL database service. Head over to Amazon DynamoDB.
- If you don't have an AWS account, sign up for one.
- Head over to the database section and select Amazon DynamoDB.
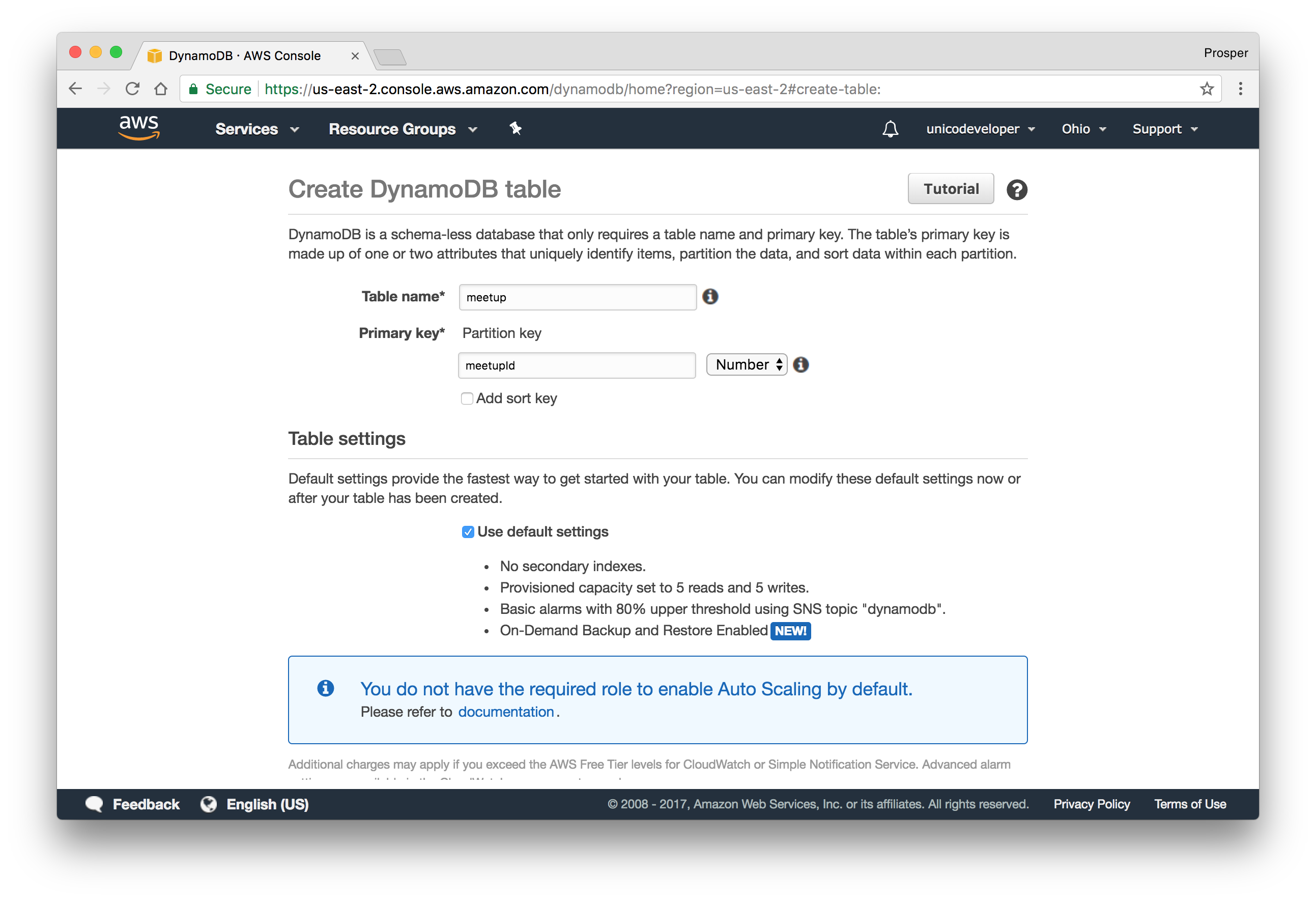
Create a table.
- Follow this instruction to install the Node.js AWS SDK, get the access key and connect to the DynamoDB table.
- You can't have more than 256 tables per account.
Microsoft Azure CosmosDB
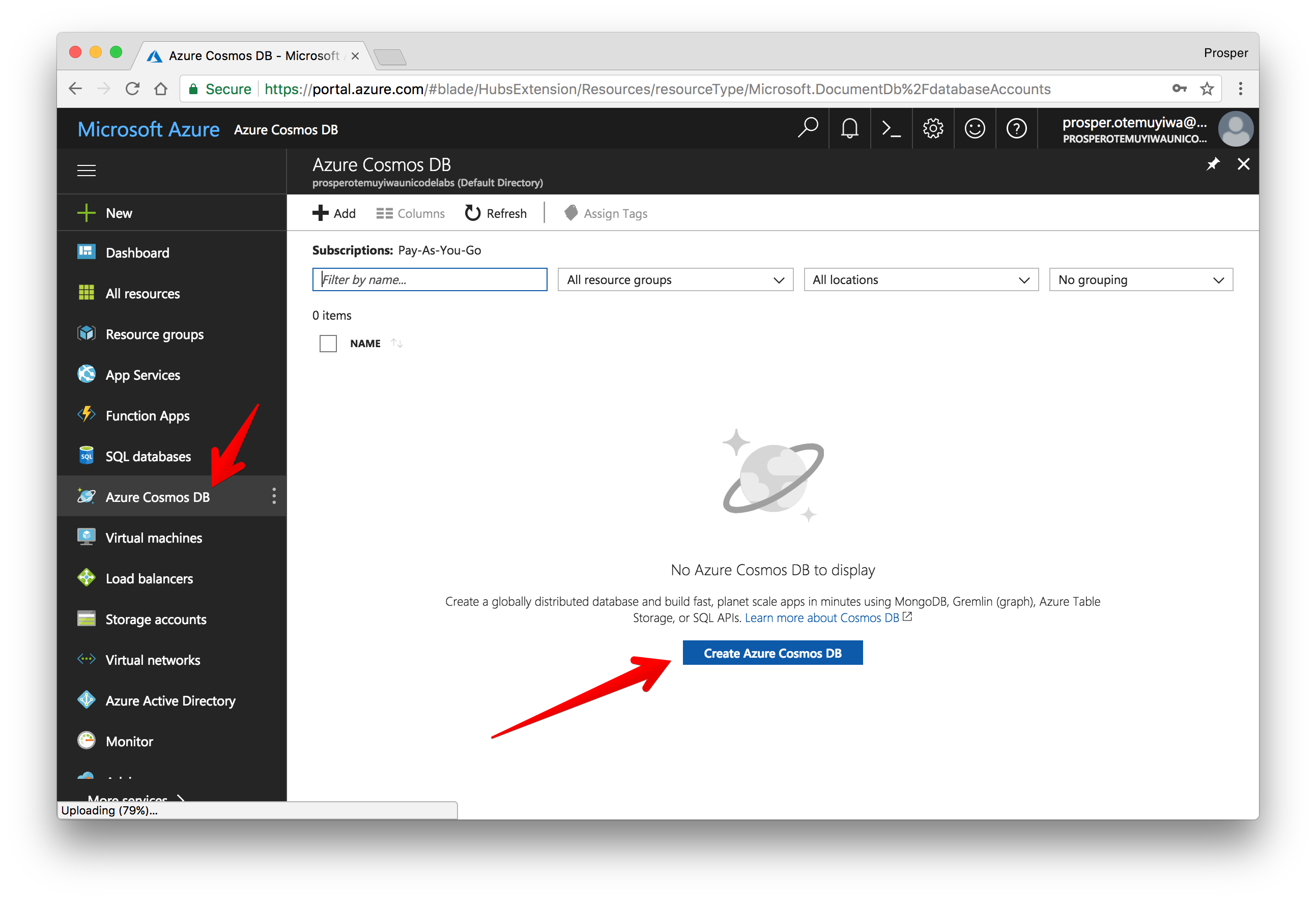
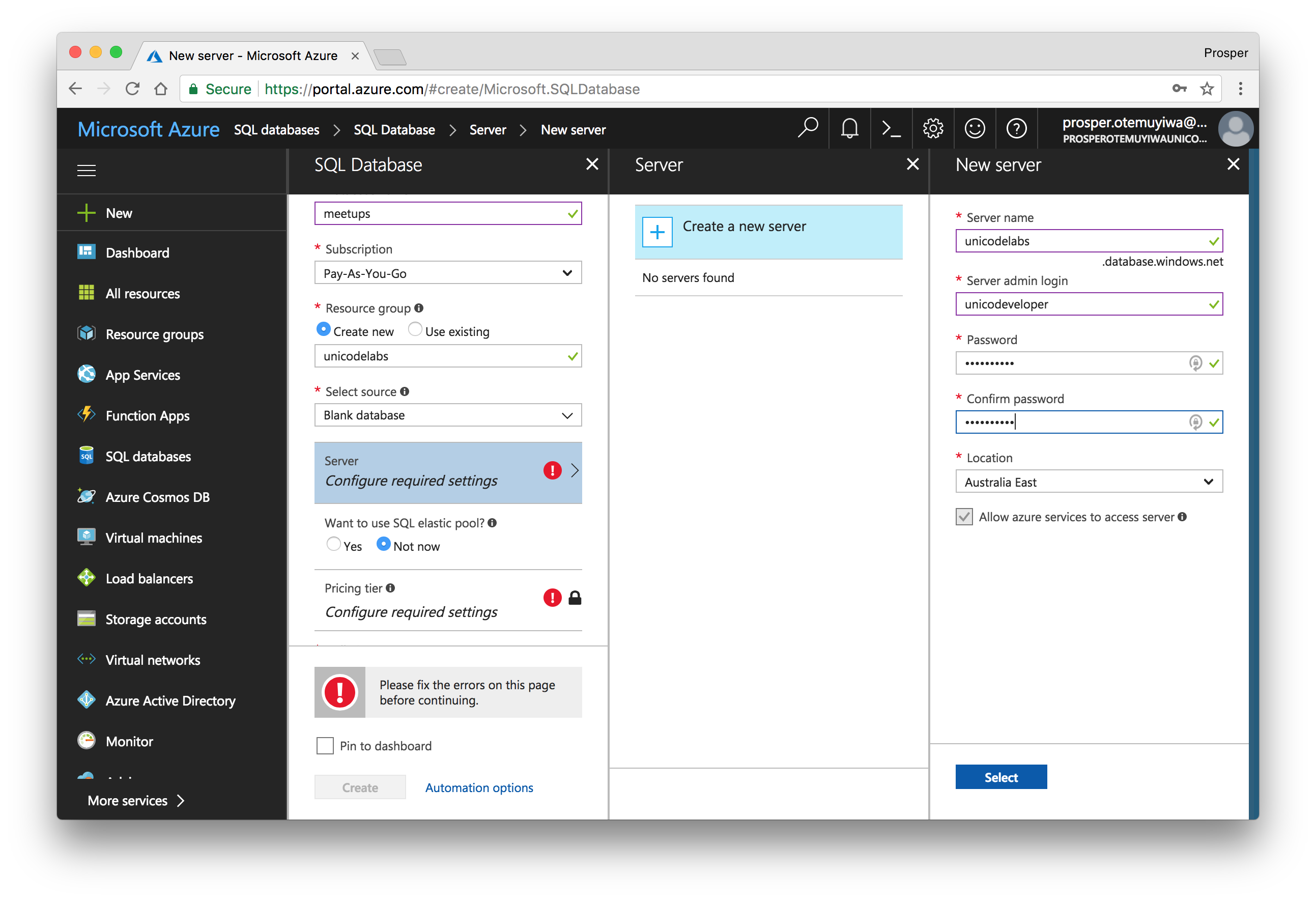
Microsoft Azure CosmosDB is a cloud platform that provides a globally distributed, multi-model database service. It provides native support for NoSQL choices, and offers multiple well-defined consistency models. To provision a database on Microsoft Azure platform, you need to follow these steps:
- Create a new account.
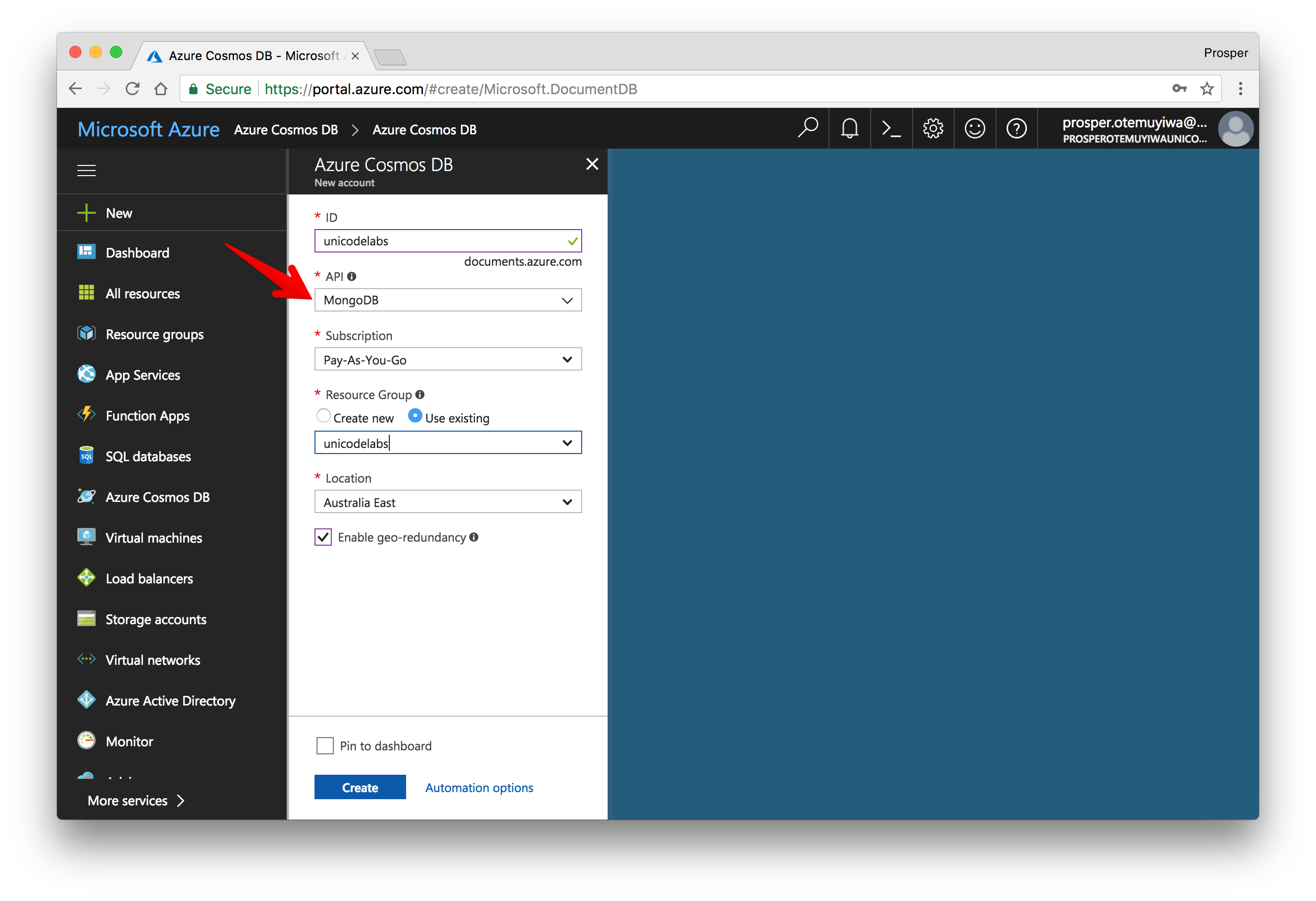
Select
by the left sidebar and create database.Azure Cosmos DBDuring creation, select the type of database you want under API.
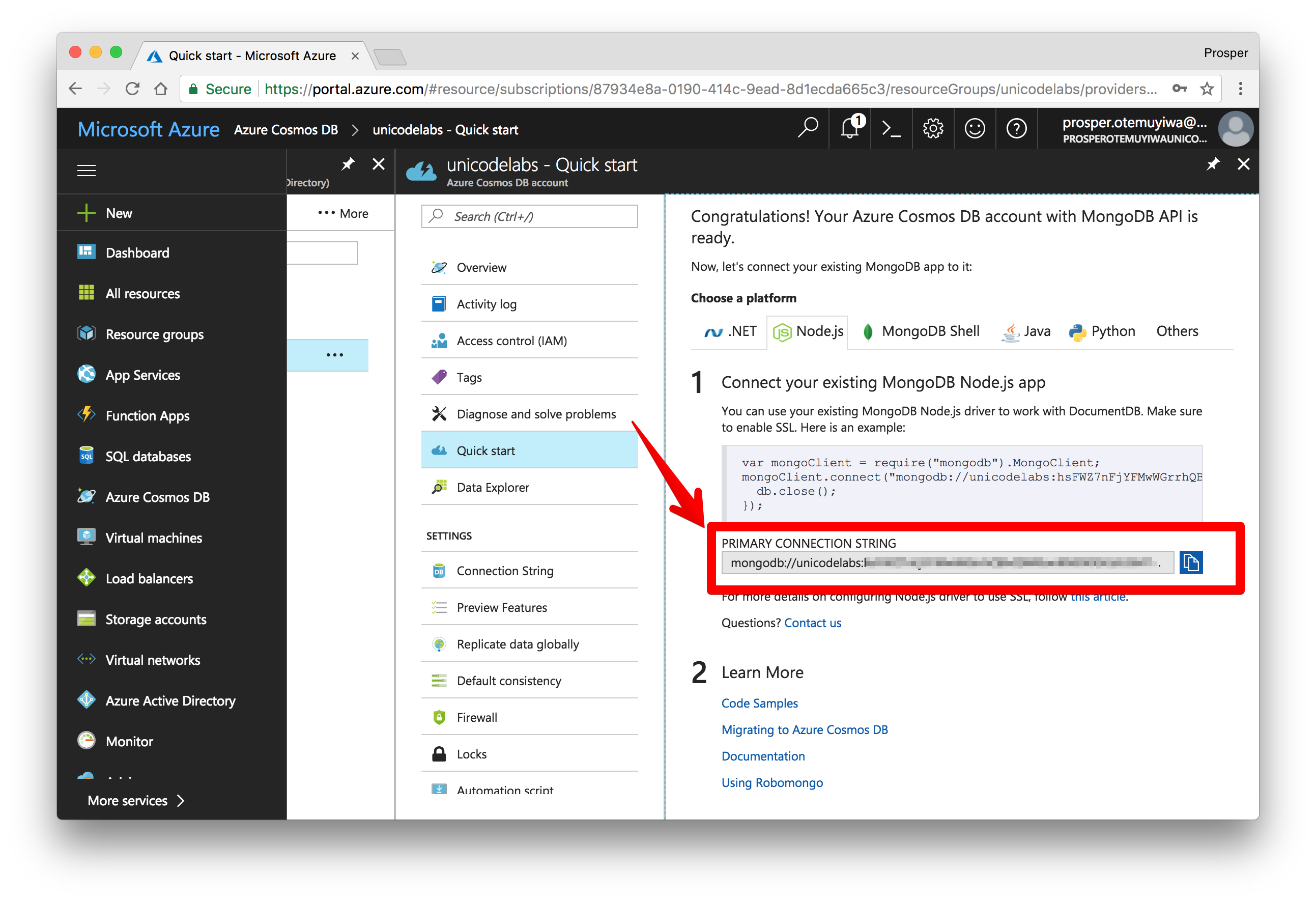
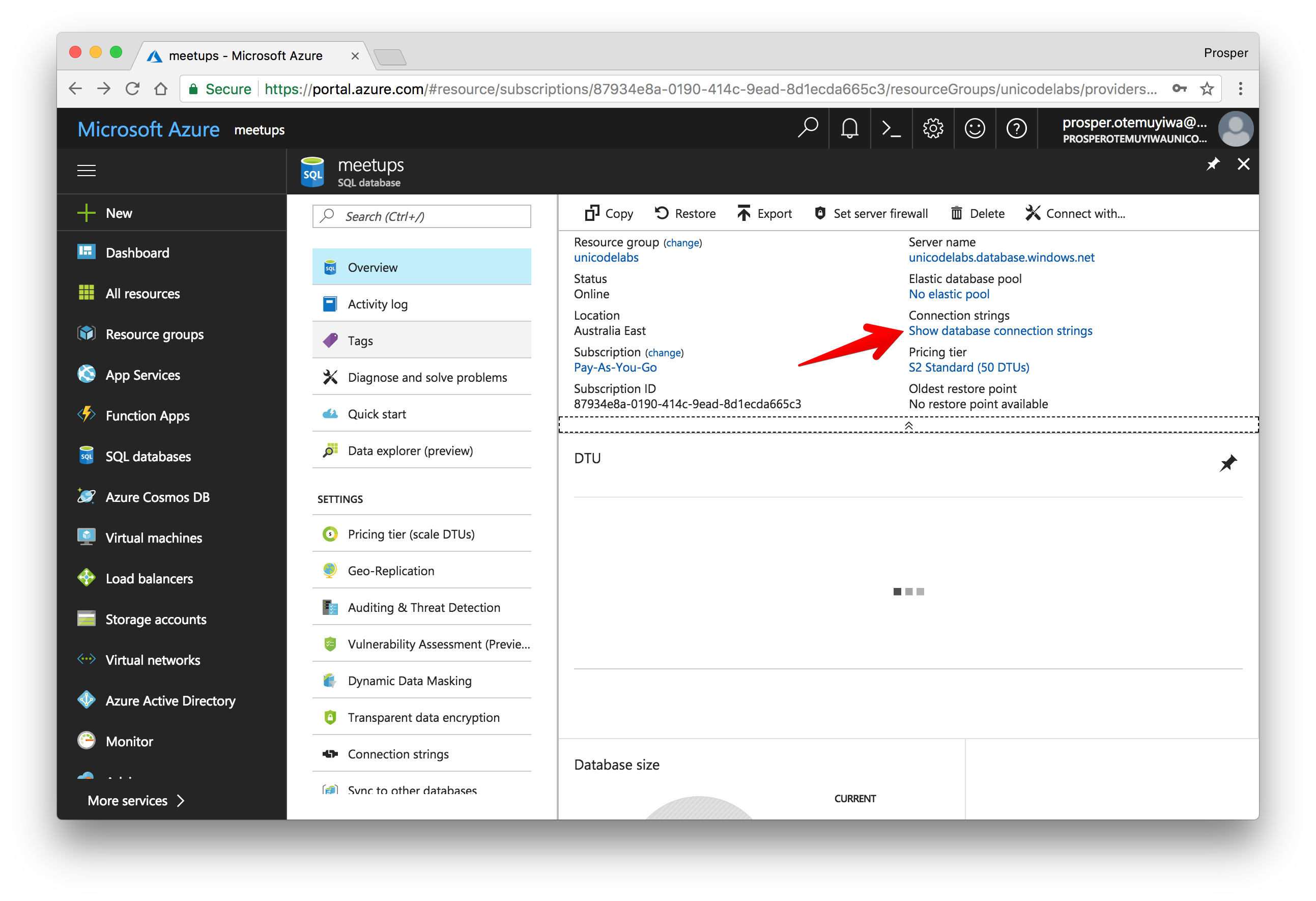
Once you are done, create the database and click on Show database connection strings.
Use the URL Connection string in your application to connect to the remote database.
Cloud Firestore
Cloud Firestore is a cloud-hosted, NoSQL database that your iOS, Android, and web apps can access directly via native SDKs. It is currently in beta release. It supports the following:
- Flexible, hierarchical data structures.
- Stores data in documents, organized into collections.
- Queries for retrieving individual, specific documents or to retrieve all the documents in a collection that match your query parameters.
- Real-time updates via data synchronization.
- Offline usage.
Follow the steps below to create a database.
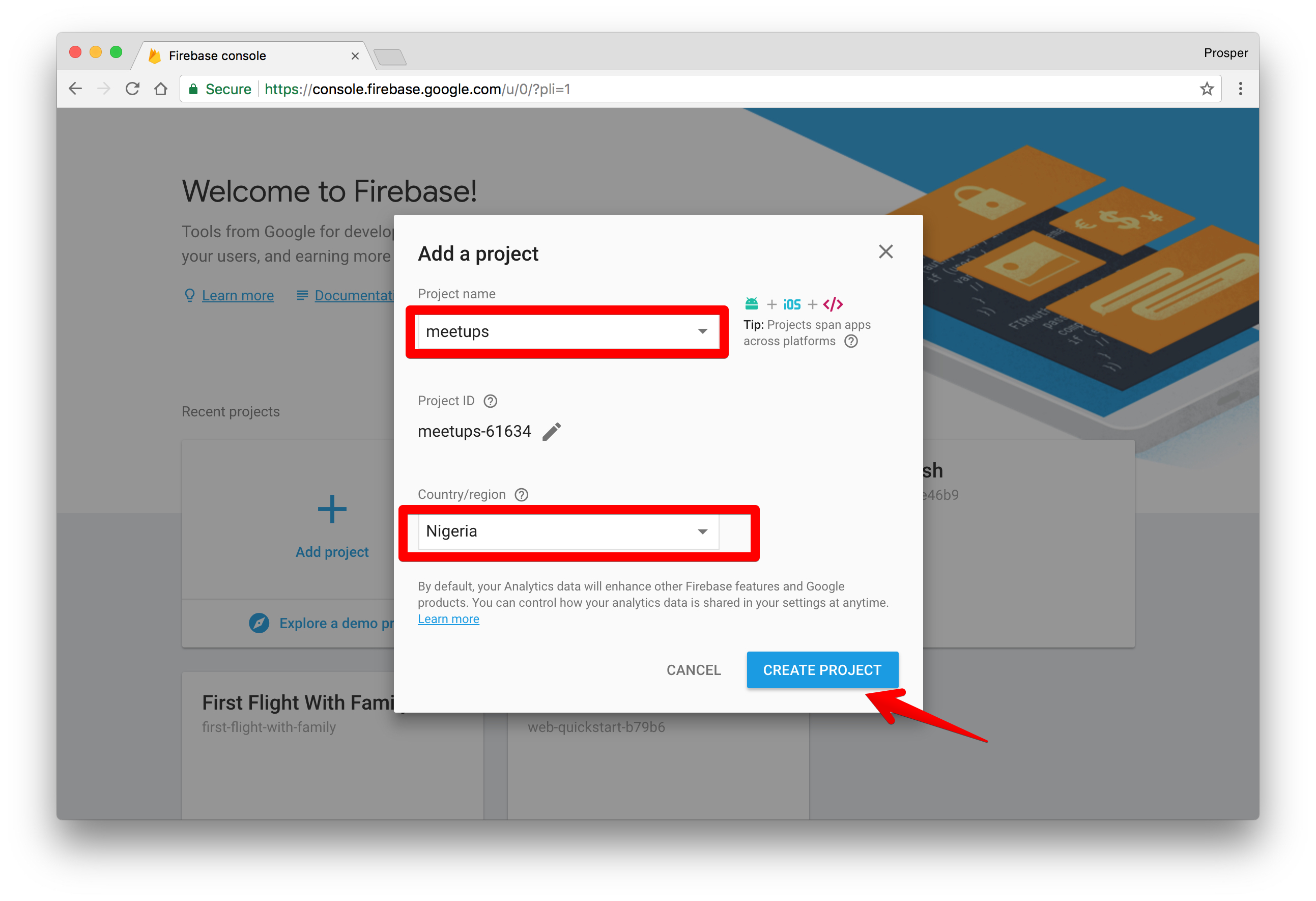
- Sign up for an account on Firebase.
Create a new project.
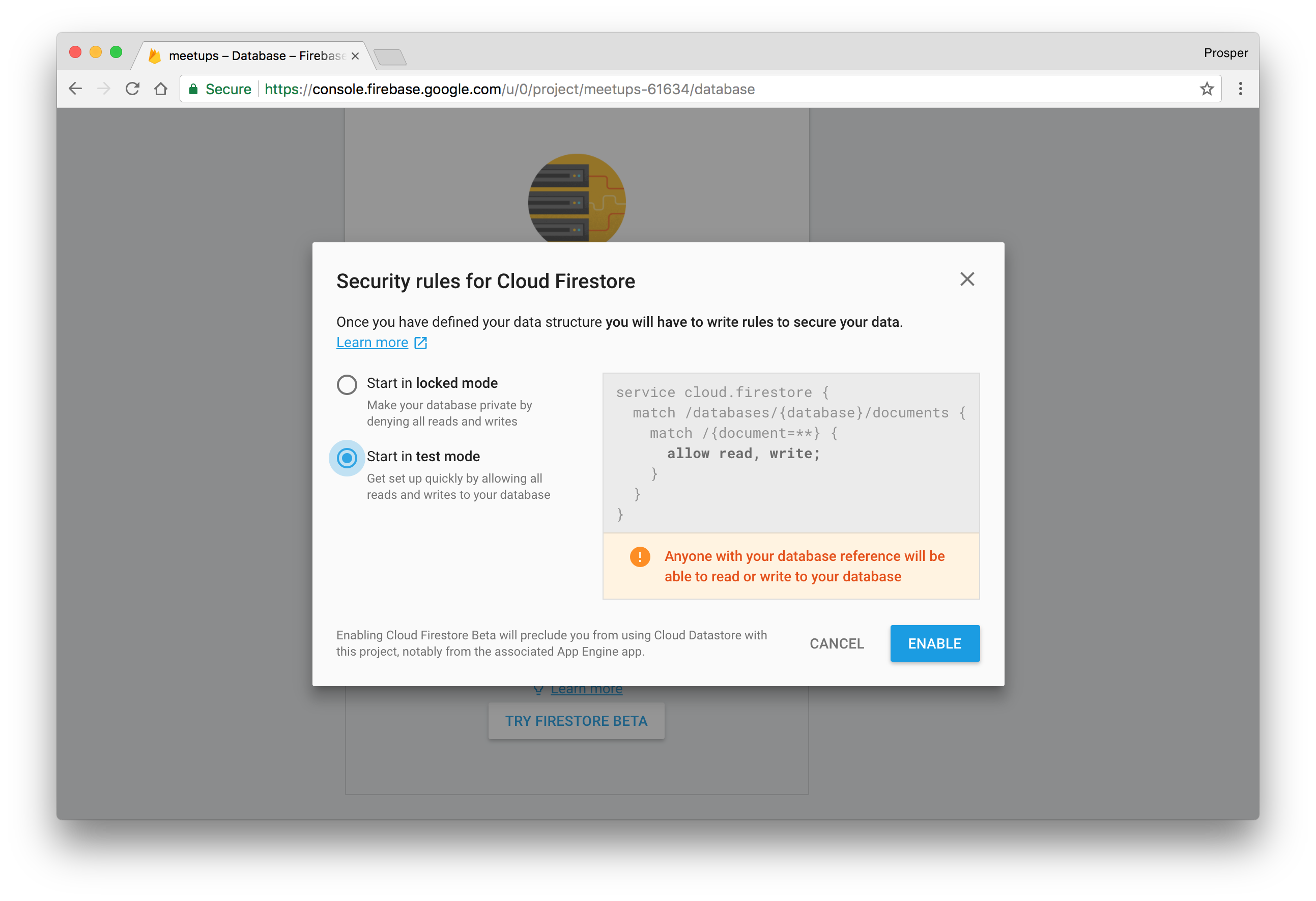
In the database section, scroll down and click TRY FIRESTORE BETA. Choose test mode to get started. However, do not forget to switch away from this mode in production.
Go ahead and install the Firebase admin SDK via
.npmnpm install --save firebase-admin@^5.5.1If your Node.js server is running on Google Cloud Platform, all you need to do is initialize it like so:
const admin = require('firebase-admin'); admin.initializeApp({ credential: admin.credential.applicationDefault() }); var db = admin.firestore();If your Node.js server is running on a different platform, you'll need a Google service account. Head over to Project Settings > Service Accounts in the Cloud Platform Console. Generate a new private key and save the JSON file. Then use the file to initialize the SDK:
const admin = require('firebase-admin'); var serviceAccount = require("path/to/serviceAccountKey.json"); admin.initializeApp({ credential: admin.credential.cert(serviceAccount) }); var db = admin.firestore();Creating a new collection,
is as easy as:meetupsvar meetupRef = db.collection('meetups').doc('meets') var publicMeetup = meetupRef.set({ 'name': 'forLoop Lagos', 'host': 'Prosper Otemuyiwa', 'attendees': '700', 'type': 'public' });Reading data from the
collection, is as easy as:meetupsdb.collection('meetups').get() .then((snapshot) => { snapshot.forEach((meetup) => { console.log(meetup.name); }); }) .catch((err) => { console.log('Error getting documents', err); });
Check out more information on using Firestore. Next, let's cover SQL databases.
Google Cloud SQL
Google Cloud SQL is a fully-managed database service that makes it easy to set up, maintain, manage, and administer your relational
PostgreSQL BETAMySQLIt offers:
- Up to 10TB of storage capacity, 40,000 IOPS, and 416GB of RAM per instance.
- Automatic data encryption.
- Google Cloud SQL is SSAE 16, ISO 27001, PCI DSS v3.0, and HIPAA compliant.
- High performance and more.
You can follow the steps below to get started with provisioning a database.
- Head over to Google Cloud SQL. If you don't have a google account, sign up for one.
Create a new project.
Create a new cluster instance.
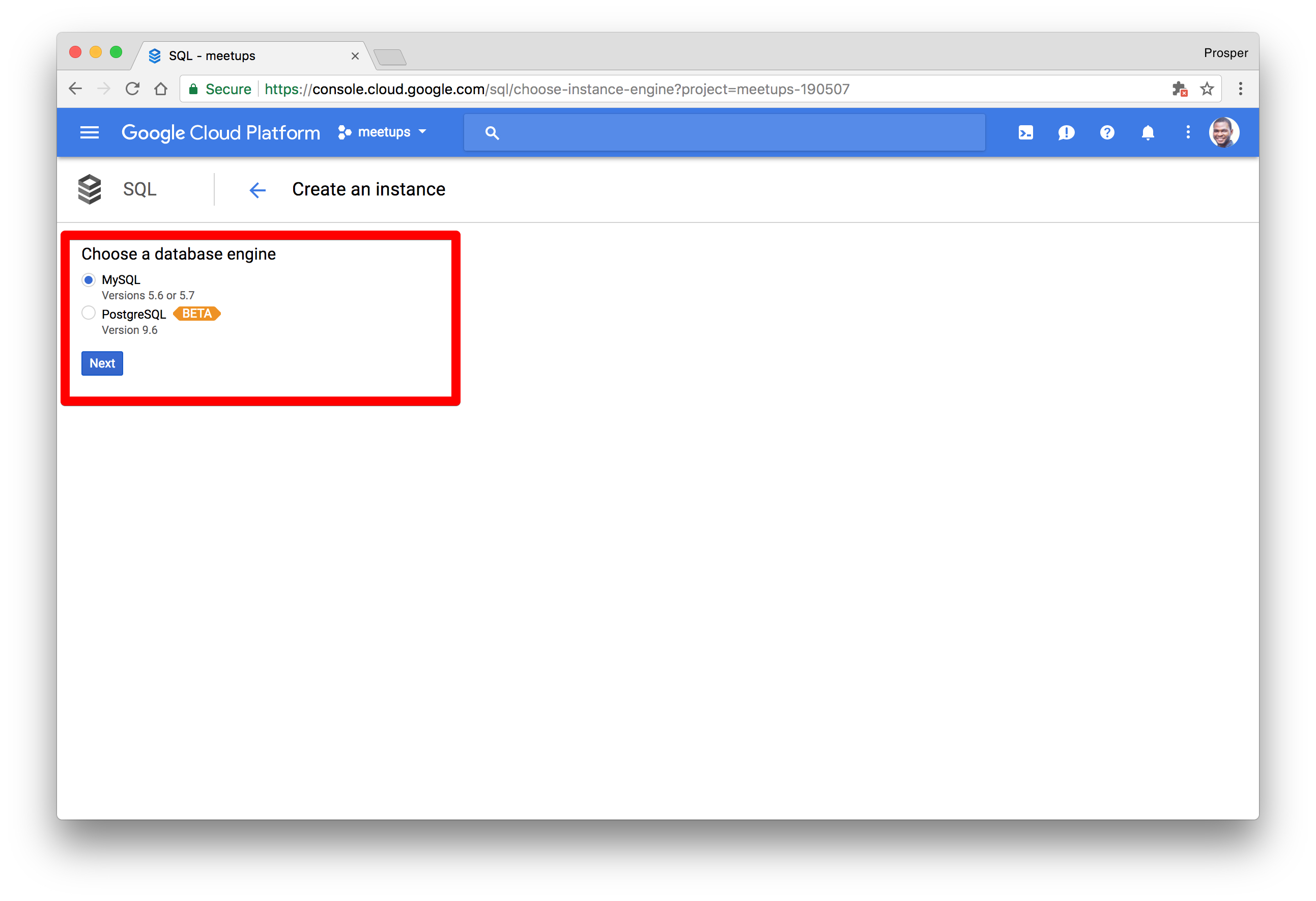
Choose the type of database, MySQL, or PostgreSQL.
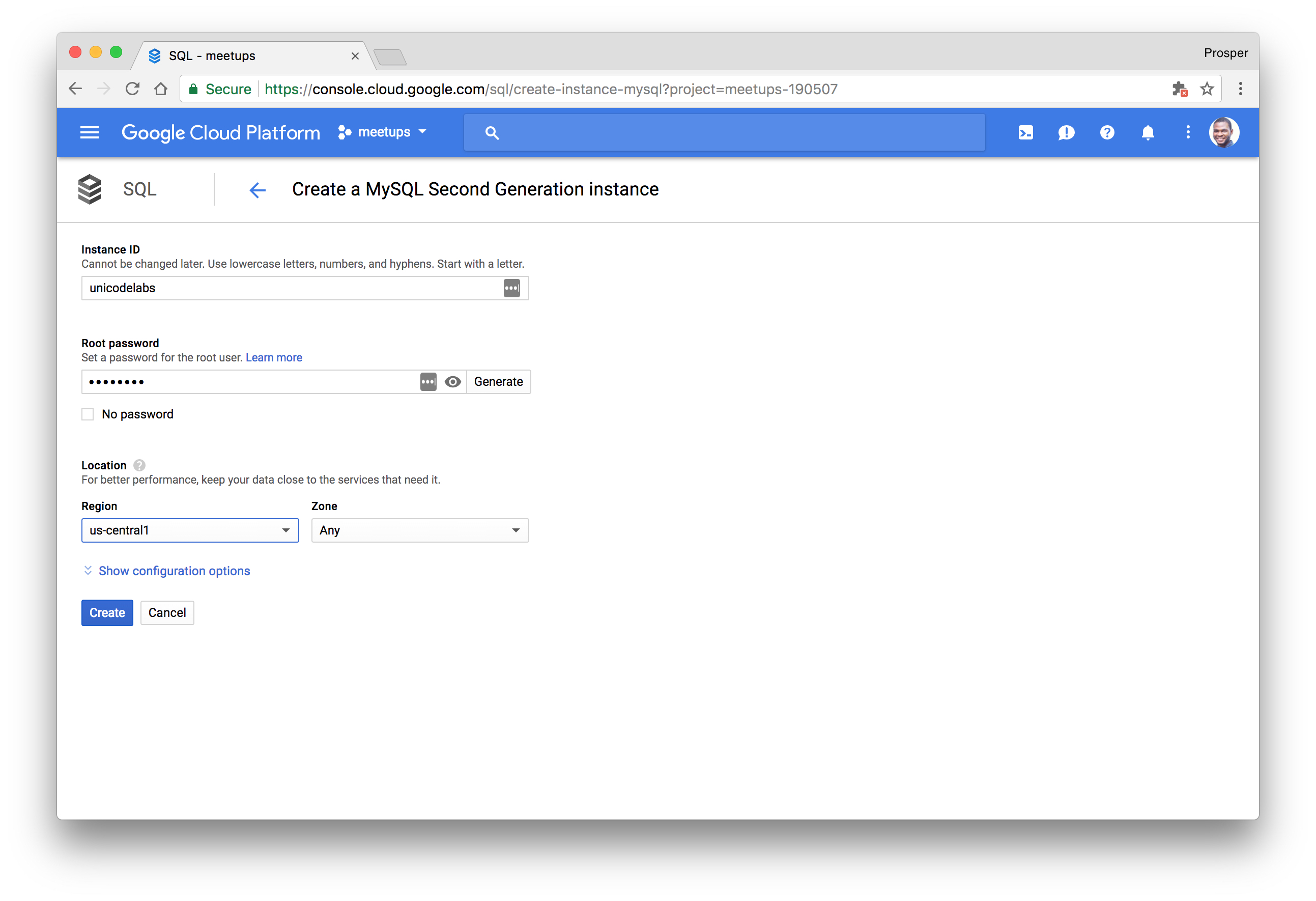
Select the region, choose an ID and password for database access and finally create the instance.
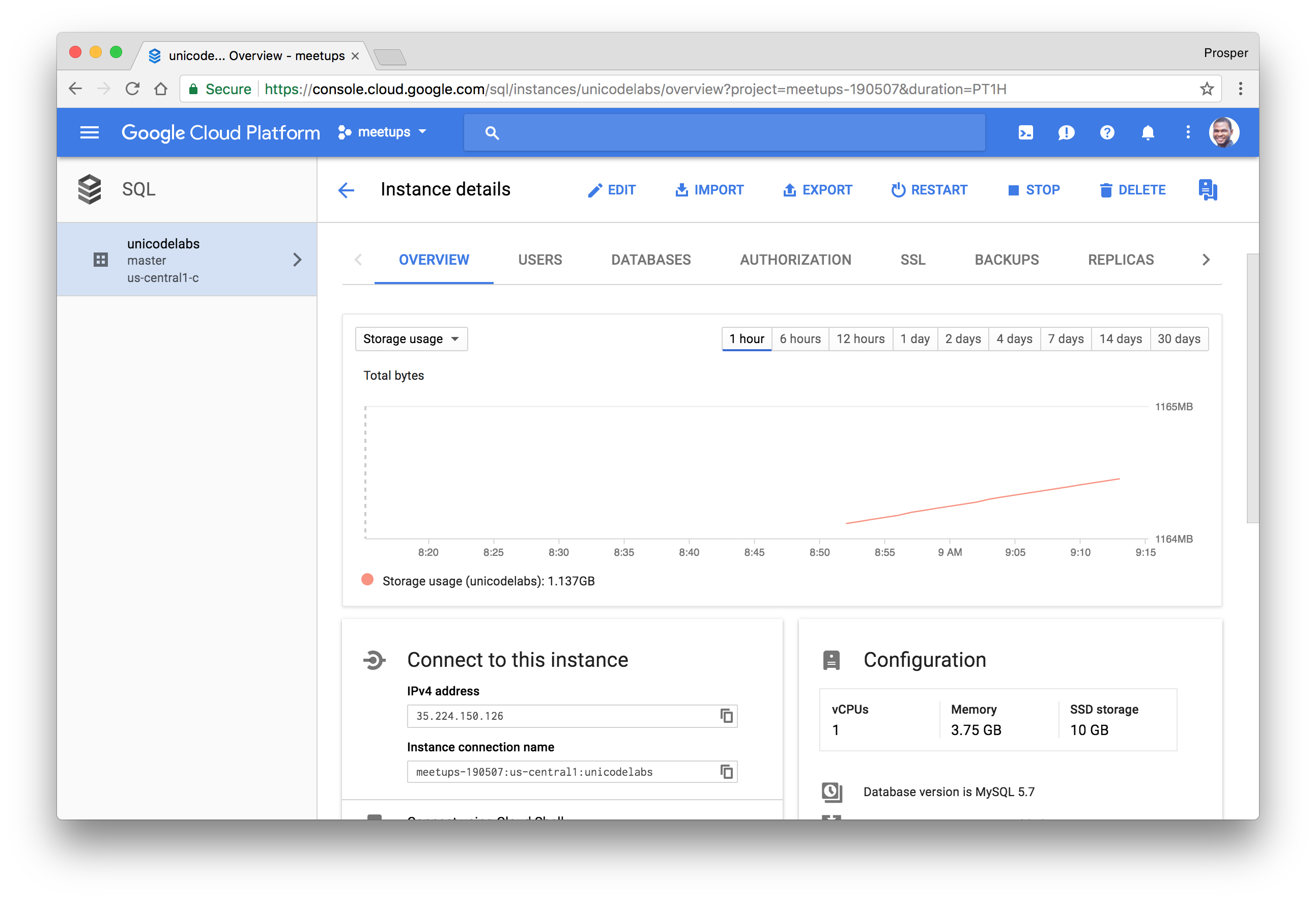
You should be presented with a dashboard after the instance has been created.
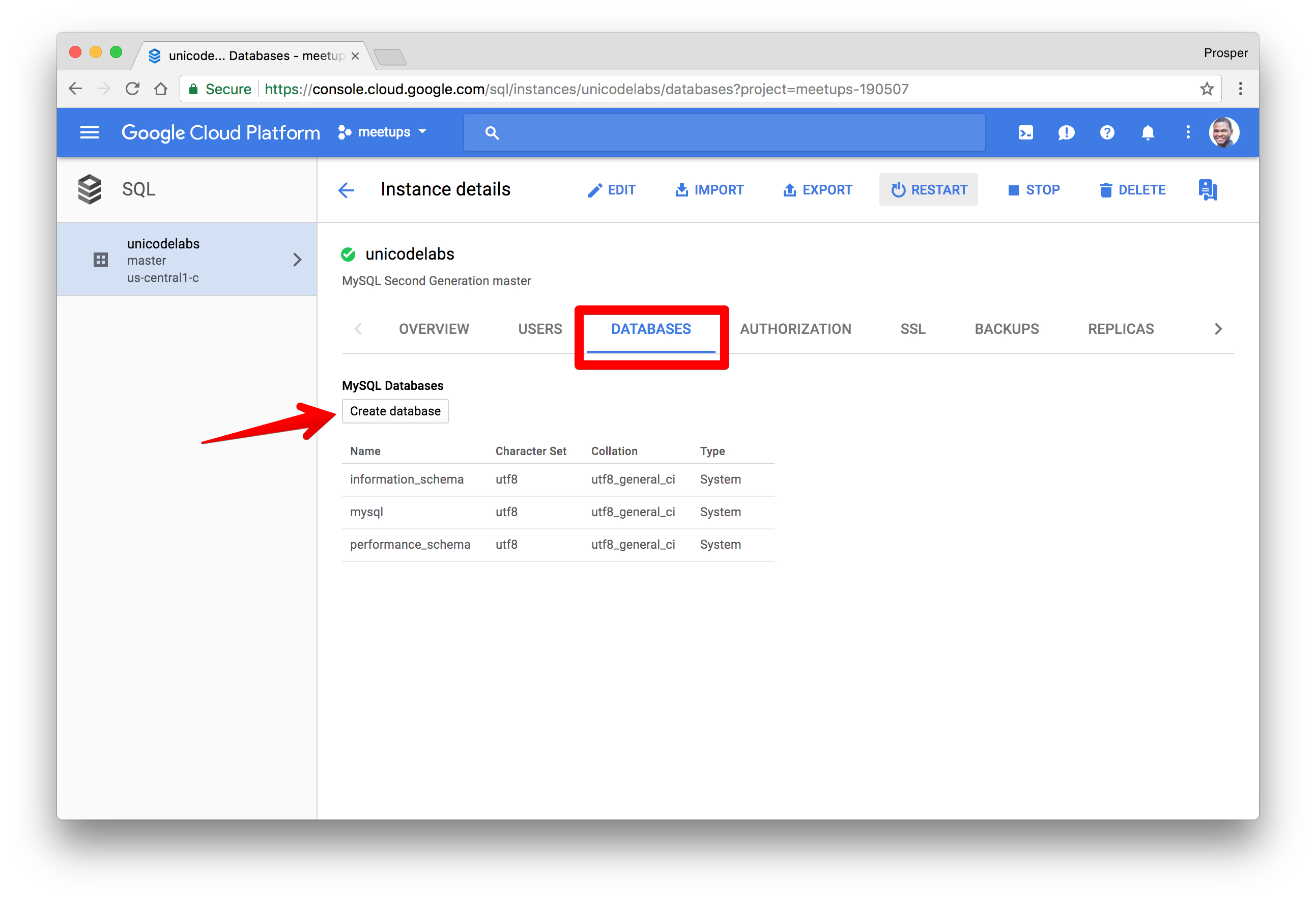
Head over to the DATABASES section and create a database for your application.
The next step is to choose the connection methods. Check out the documentation on the connection options for external applications.
Elephant SQL
Elephant SQL is a cloud platform that offers PostgreSQL as a service. It offers a shared and dedicated instance. The free shared instance offers 20MB data storage and 5 concurrent connections.
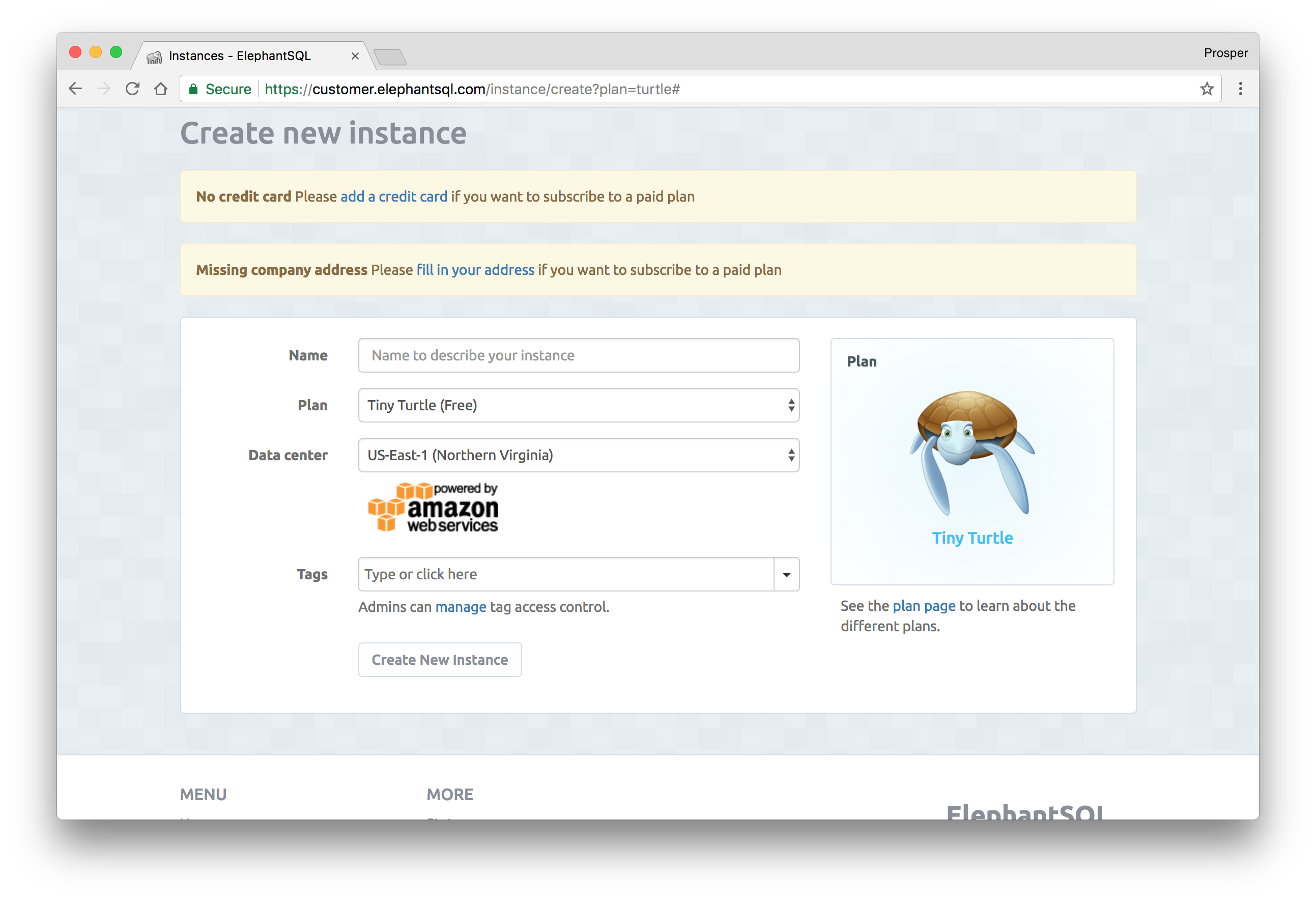
You can follow the steps below to get started with provisioning a database.
- Create a new account.
Create a new instance.
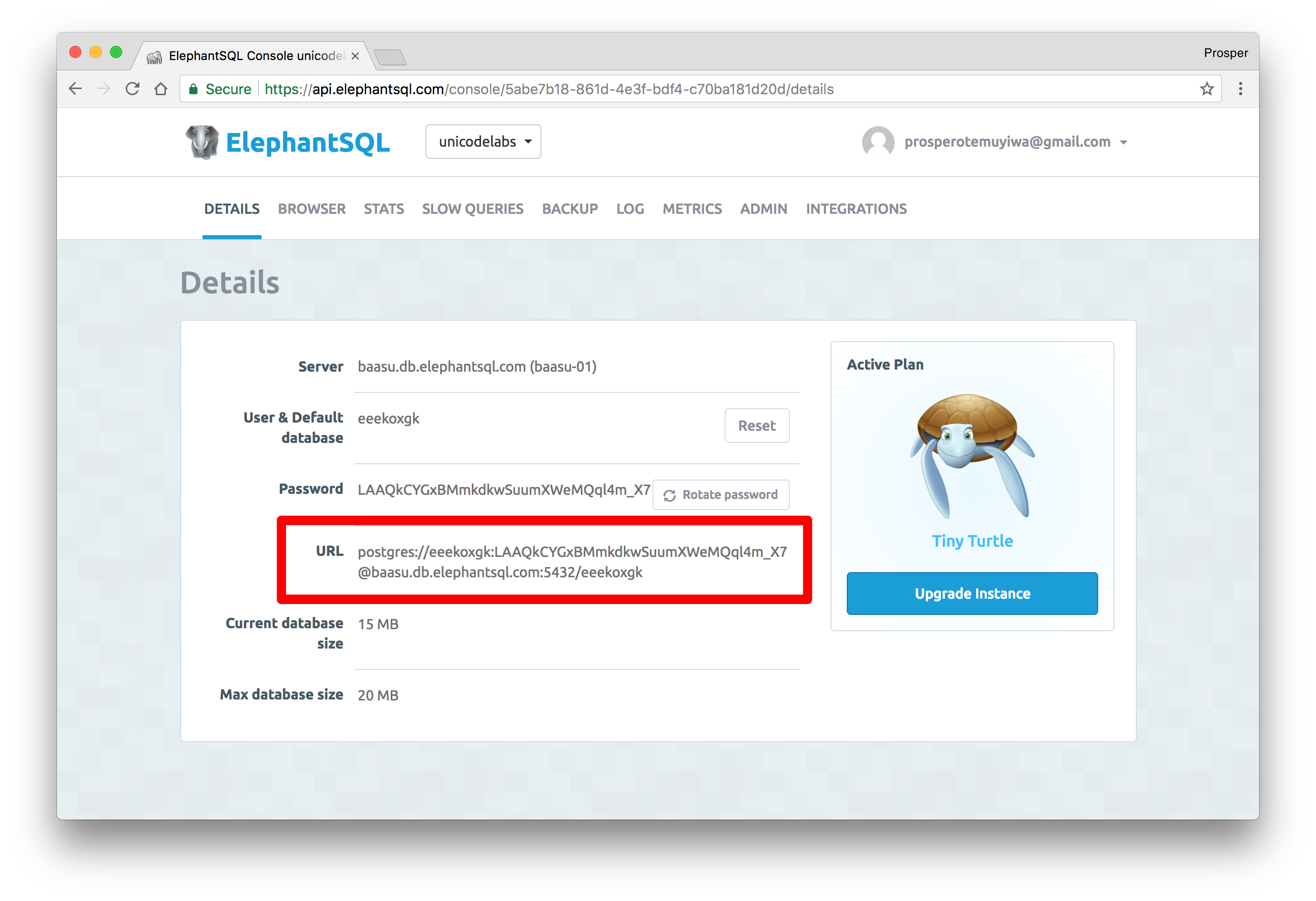
Click on the recently created instance. You'll be directed to a dashboard that shows the URL connection string.
Use the URL Connection string in your application to connect to the remote database. It's really simple.
Microsoft Azure SQL
Microsoft Azure SQL is a cloud platform that offers SQL Server as a service.
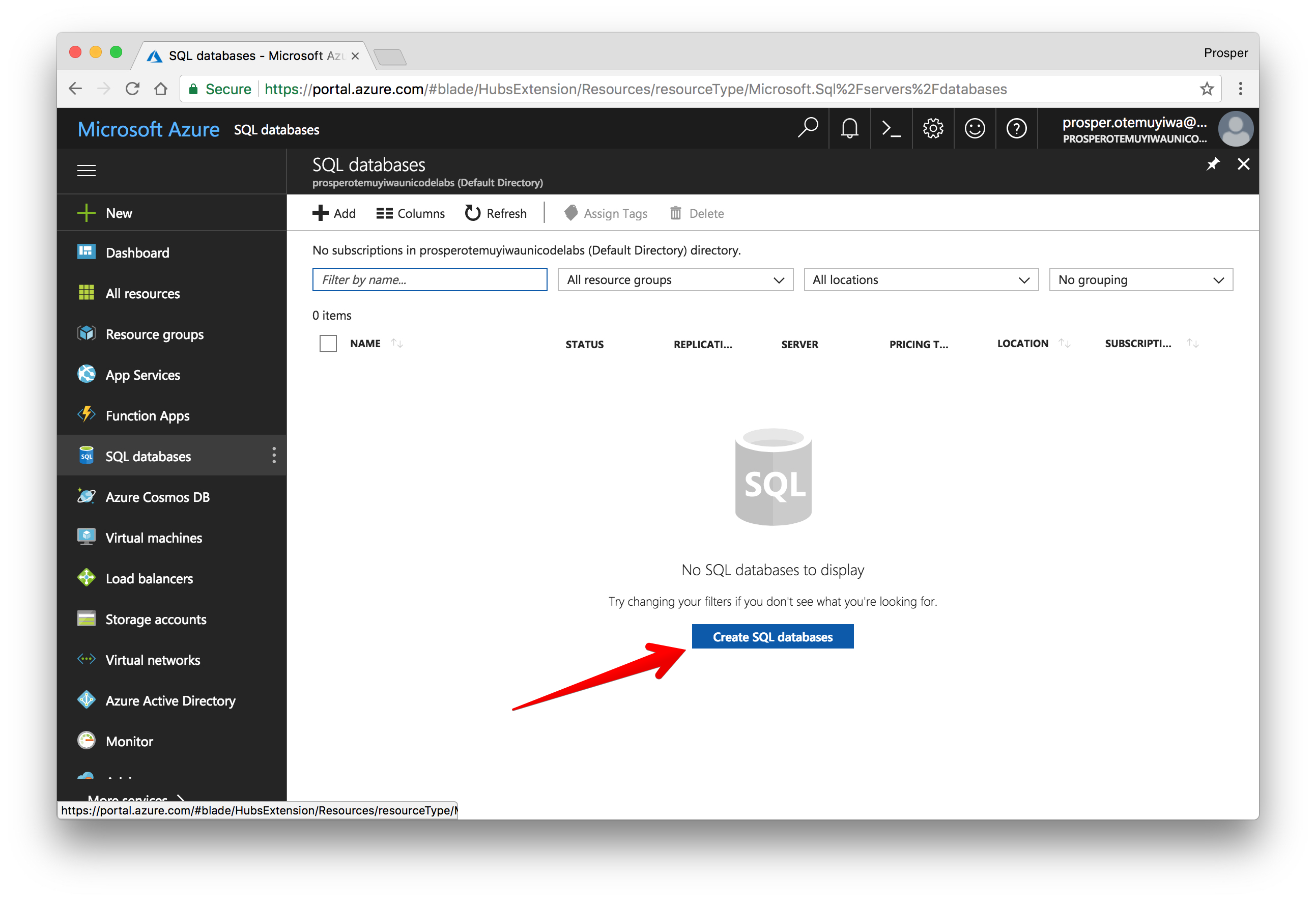
You can follow the steps below to get started with provisioning a database.
- Create a new account.
Select
by the left sidebar and create database.SQL DatabasesDuring creation, create a new server by filling in the right details and clicking on
.SelectOnce you are done, create the database and click on Show database connection strings.
Use the URL Connection string in your application to connect to the remote database.
Amazon RDS
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) is a cloud platform that makes it easy to set up a relational database. It provides six popular database engines:
It is highly optimized for memory, I/O and performance.
Code Deployment
We have briefly discussed the several ways and services you can deploy your database. Now, let's talk about the code. Here, we'll deploy the backend. There are several awesome cloud platforms that do a very awesome job at backend deployments.
Heroku
Heroku is a cloud platform that helps you deploy and host your applications the modern way. It does all the heavy-lifting for you. Let's quickly take a look at how to deploy and maintain a Node.js application on heroku.
Heroku runs a first-class experience for Node.js so every developer can run successful production apps.
If you don't have an account, go ahead and create one on heroku.com. Go ahead and install the Heroku CLI.
Heroku runs your Node.js app in a dyno, a smart container which provides a modern stack with your choice of web server and runtime.
Clone the backend from GitHub.
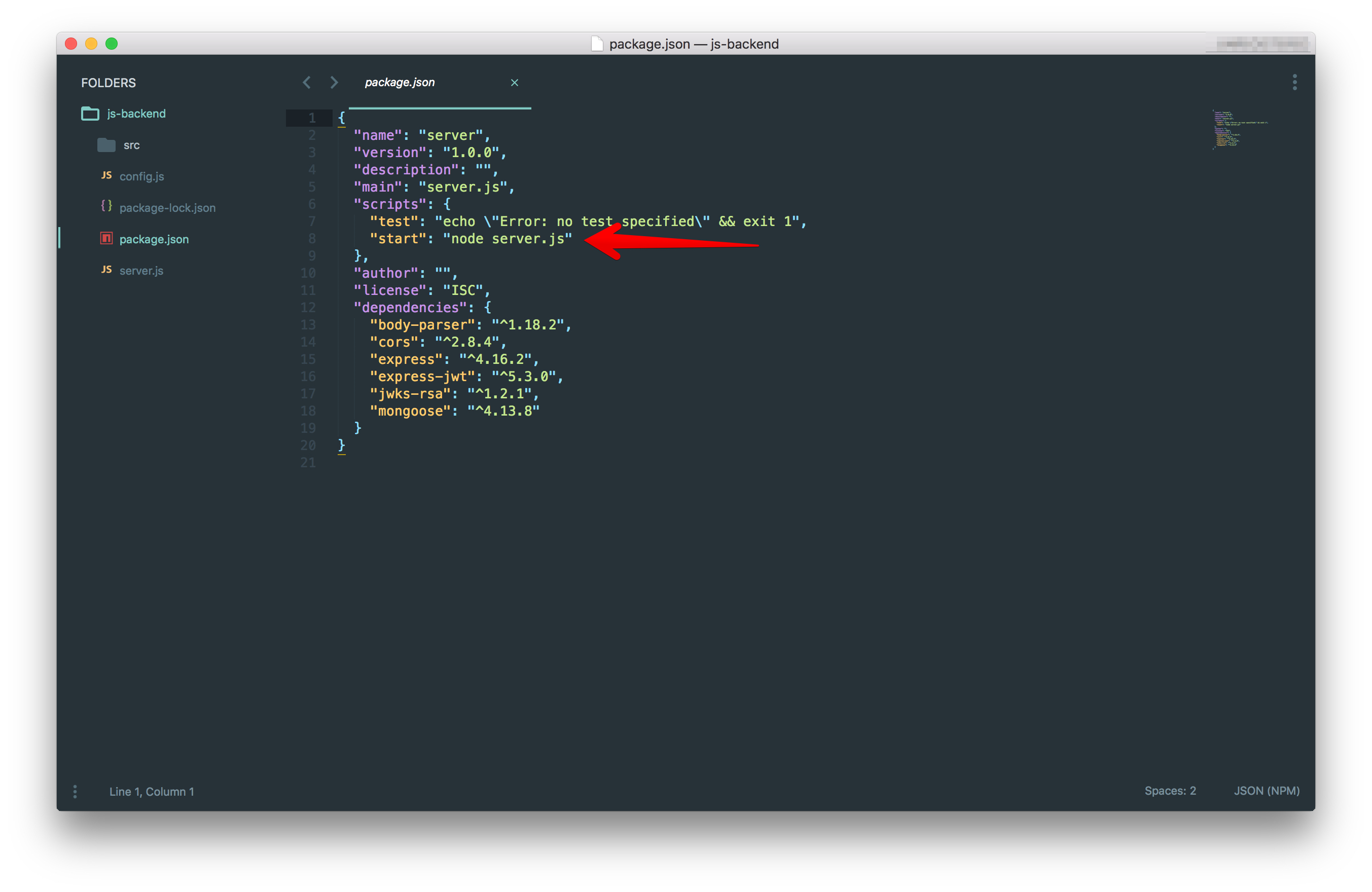
Heroku looks for a Procfile. If no
Procfilestart scriptpackage.jsonstart scriptNote: A Procfile is a text file in the root directory of your application that defines process types and explicitly declares what command should be executed to start your app on Heroku.
You can go ahead to upload the project to your GitHub or Bitbucket account.
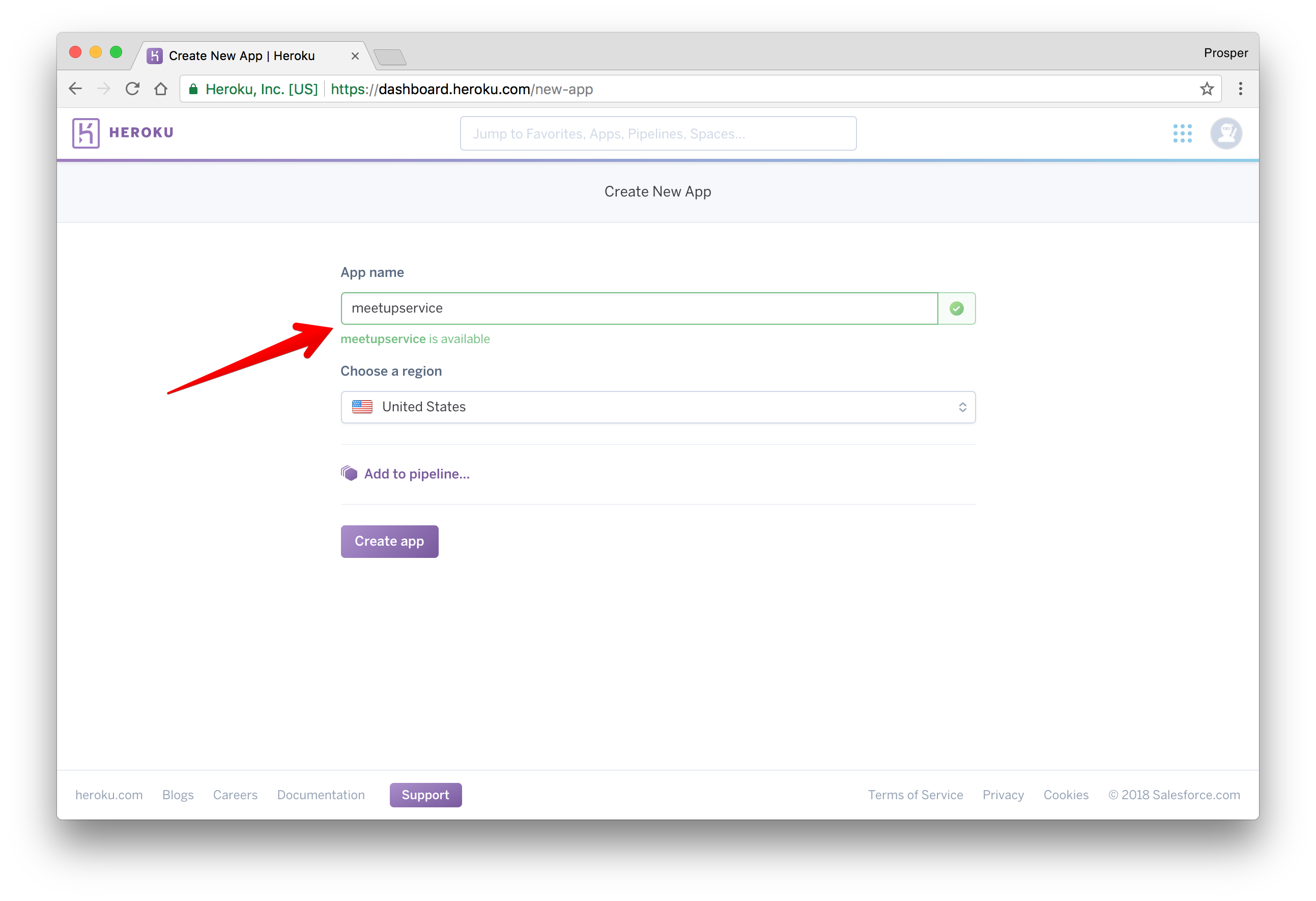
Head over to dashboard.heroku.com/apps and create a new app like so:
Give it a name like so:
Choose a deployment method. In our case, we'll use GitHub like so:
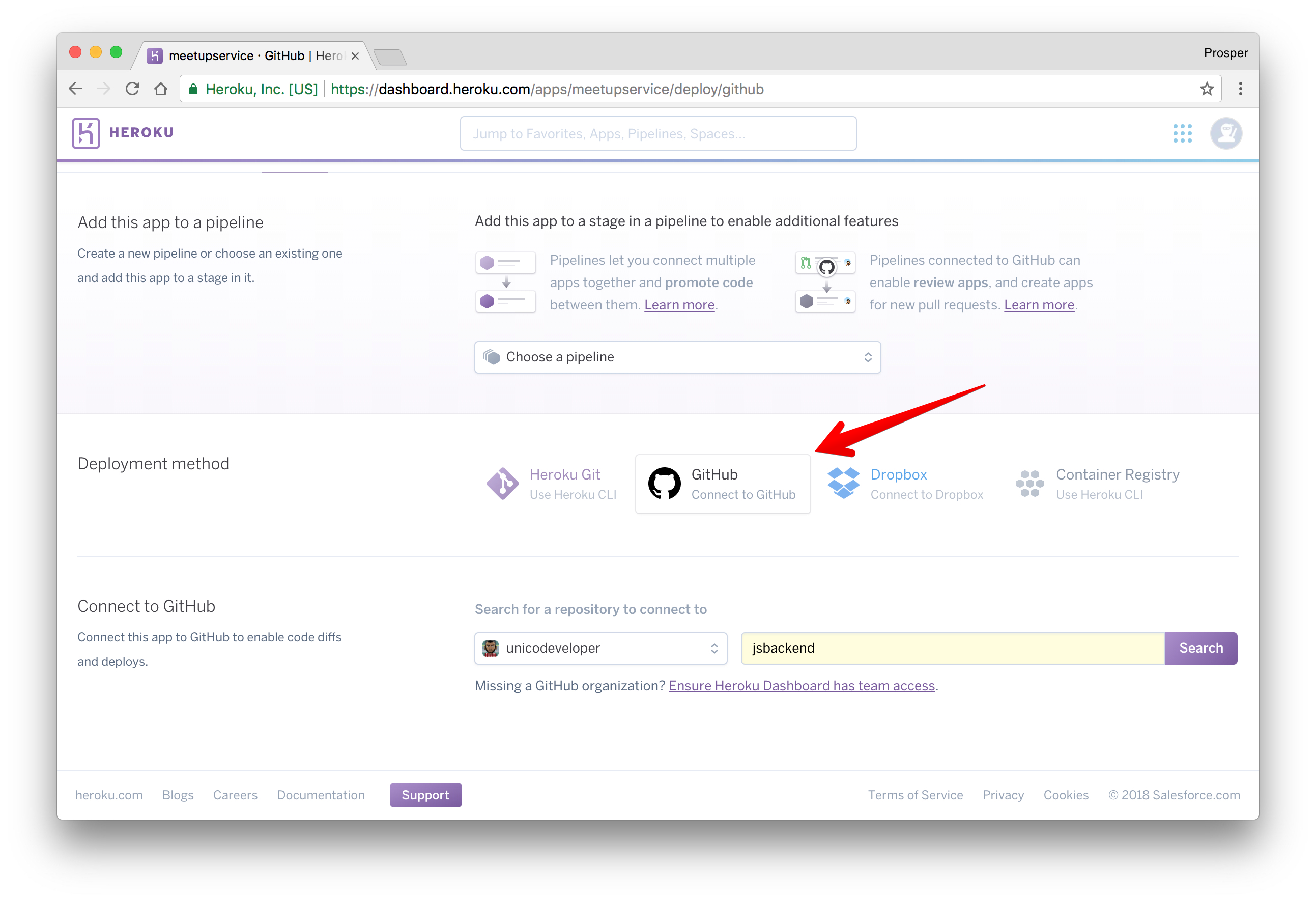
The reason for choosing GitHub is to make development and maintenance process very smooth. Developers can work on new features using the git workflow.
Now, type the name of the repo in the circled area and click Search. Heroku will search for your repo under your GitHub account and display it like so

Click on
connect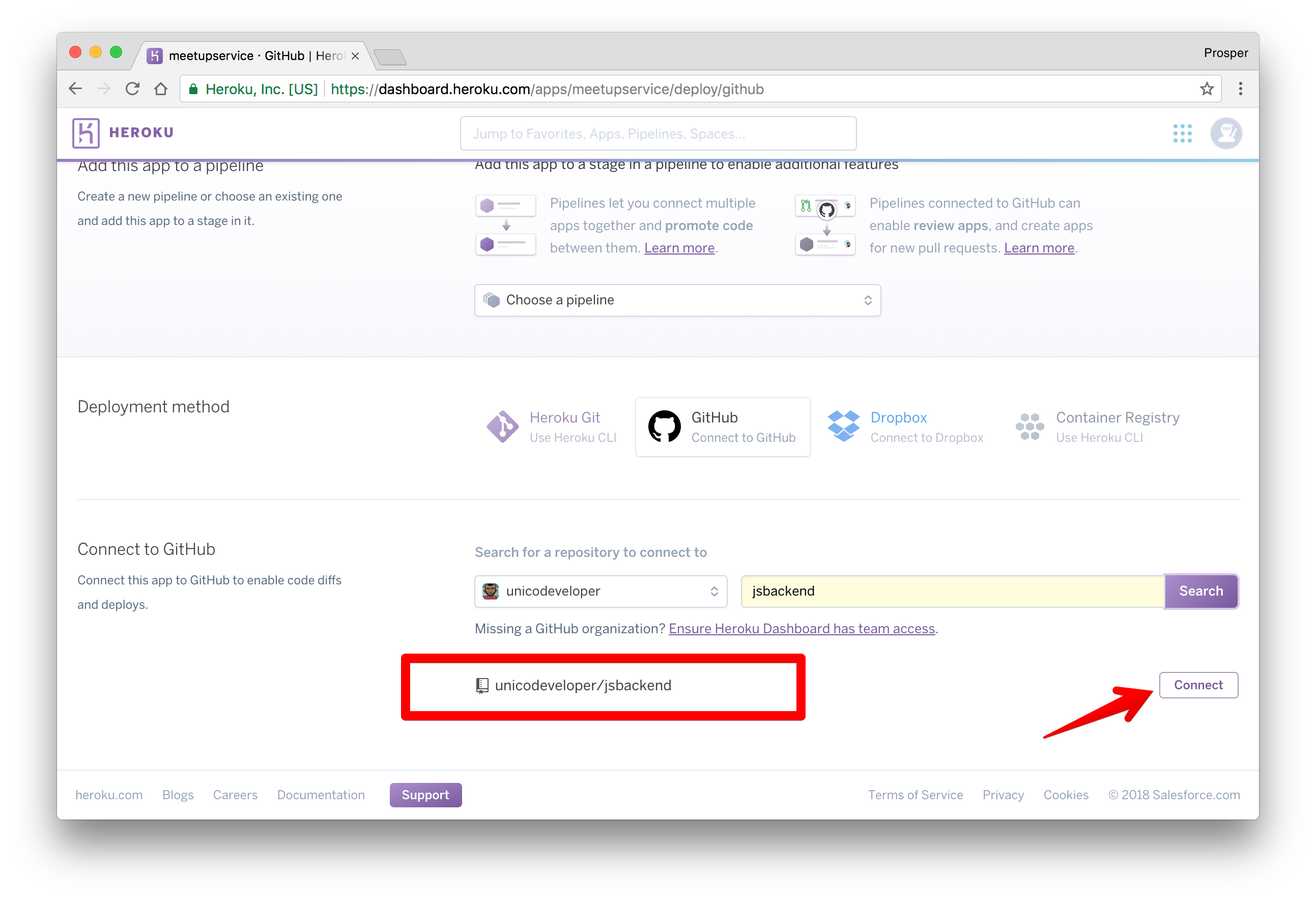
Heroku will connect the repo like so
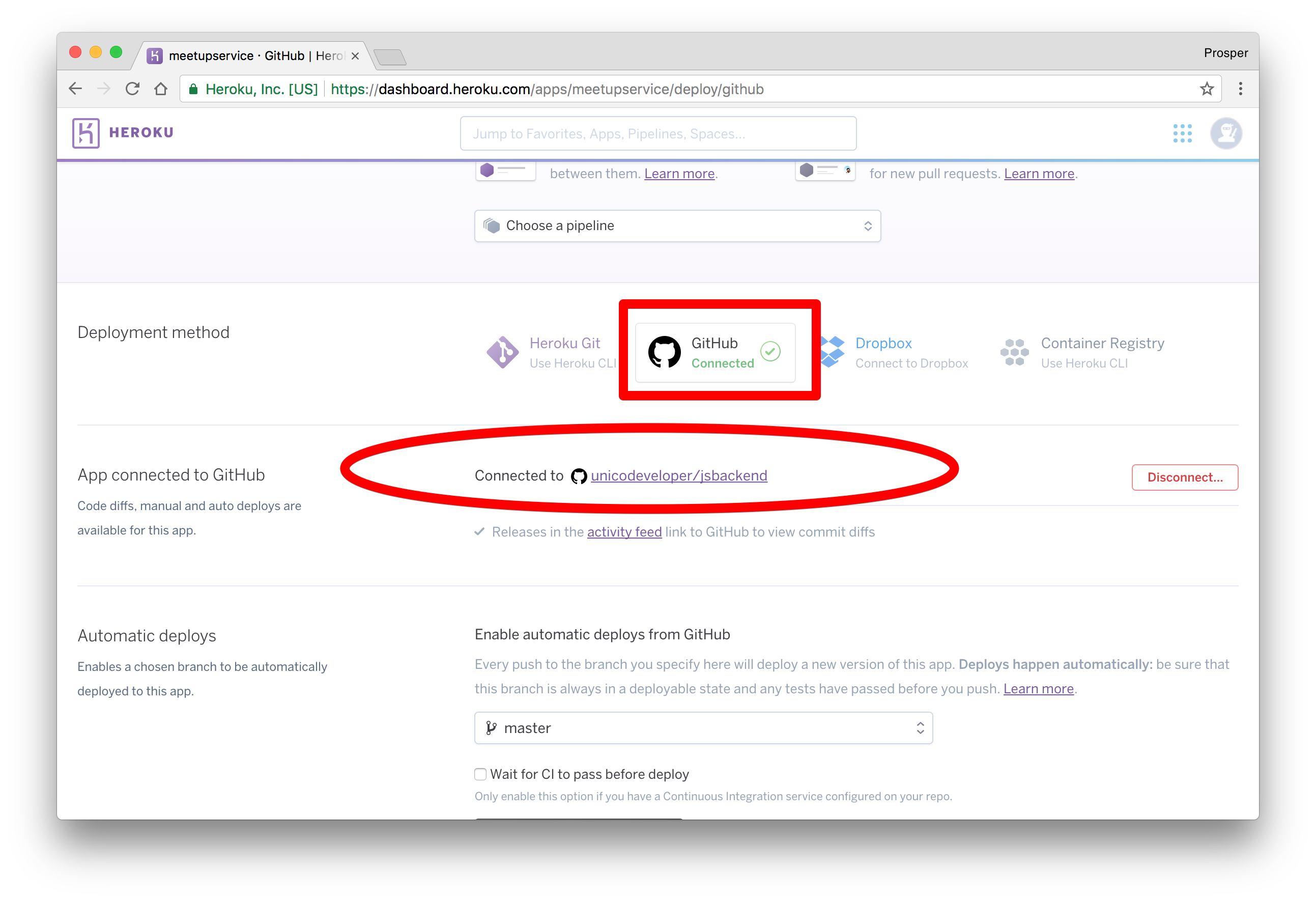
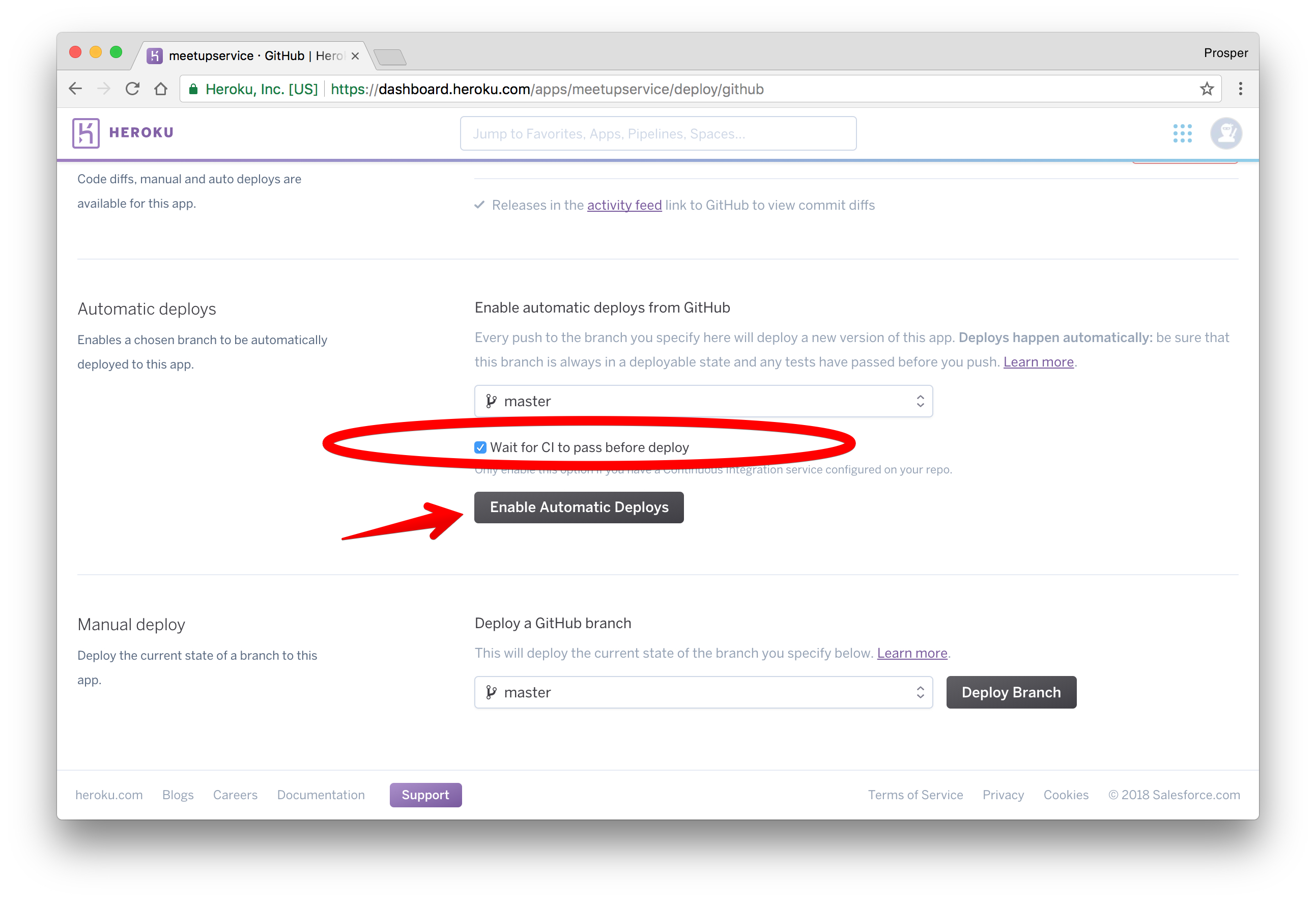
Scroll down a bit. This is the interesting part. Heroku allows you to enable automatic deploys with the push of a button. It also gives you an option to wait for your continuous integration process to pass before deploying to production. In a real world app, you'll have a test suite for your codebase. A developers' code runs against the test suite. If it passes, the code will be pushed to production.
Click to enable automatic deploys. We don't have any CI service, so we don't need to enable that option. Now, let's deploy the master branch.
Note: You can have other branches and specify which branch you want for production. In our case, the master branch is the prod. branch.
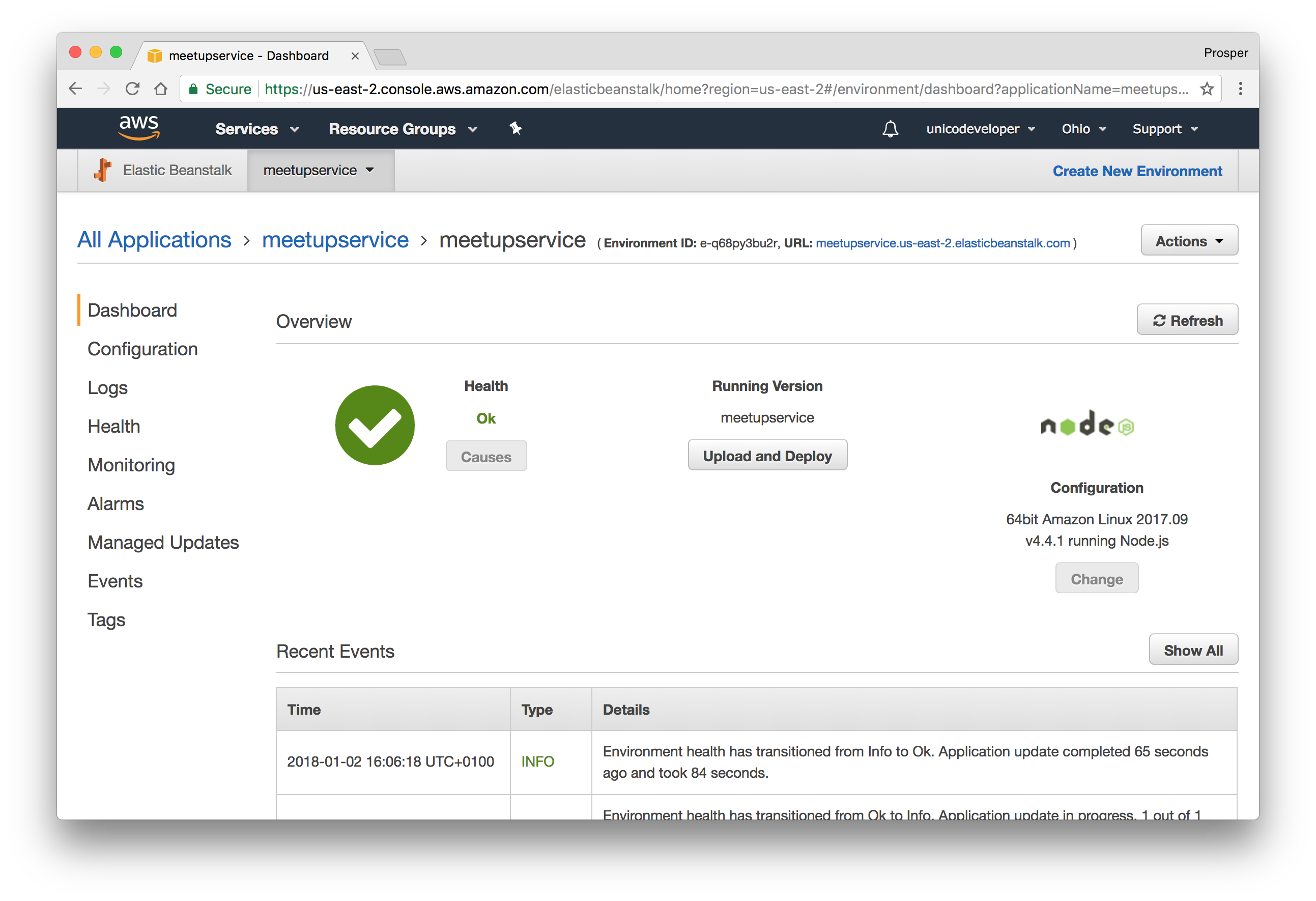
Click on the Deploy branch. Heroku will scan through your
package.json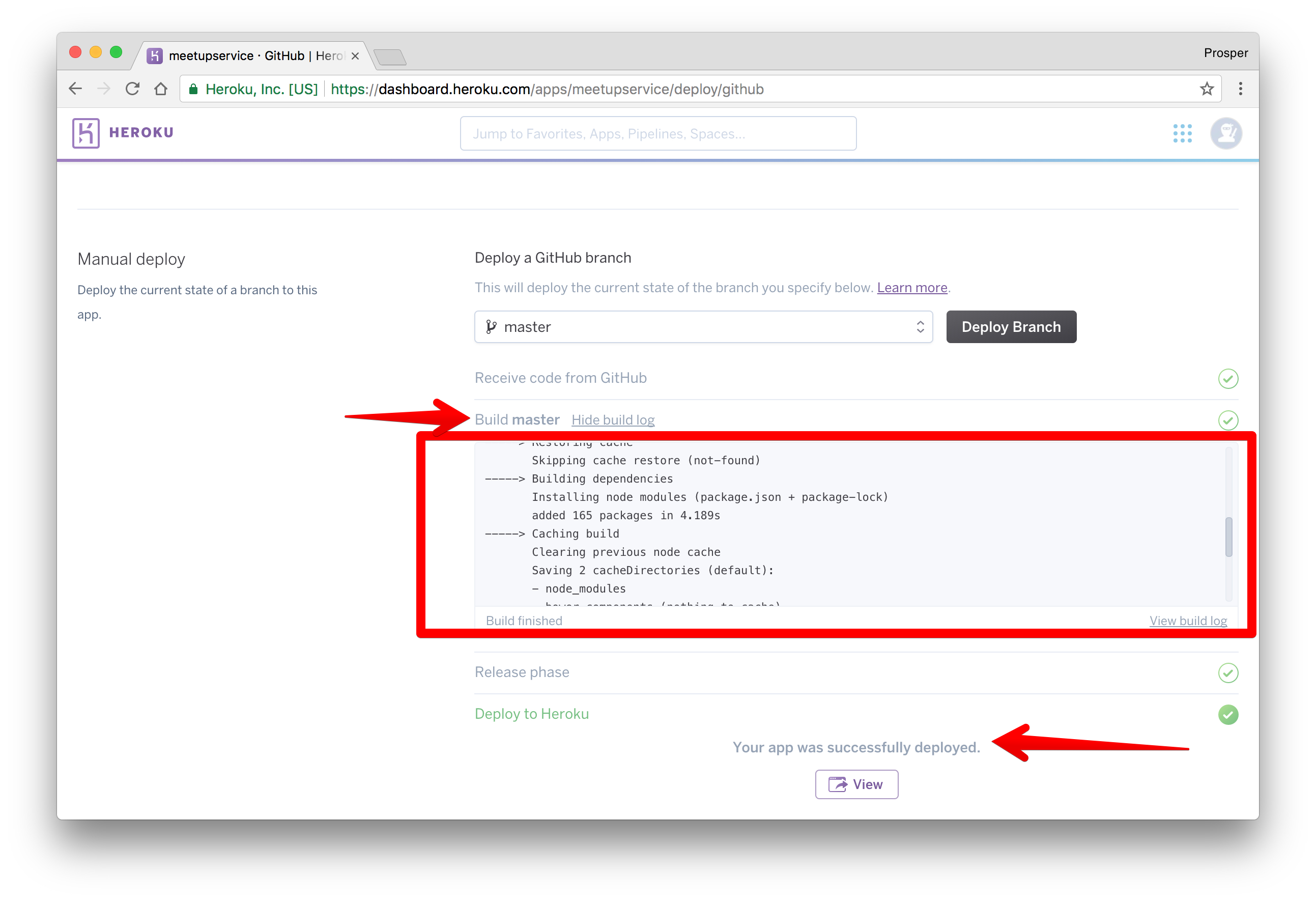
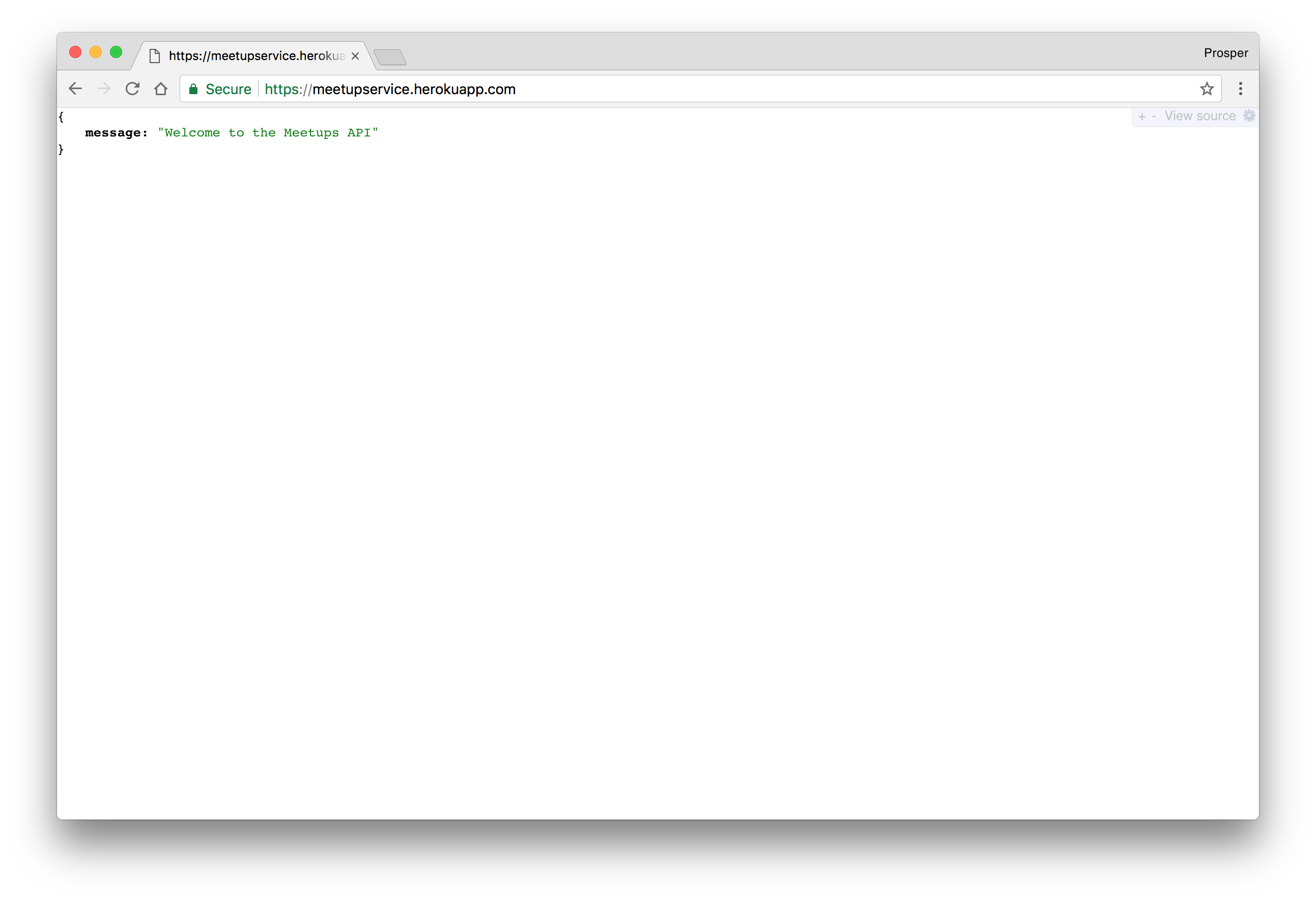
Click on the View button to check out your app. Now, we don't have any root route, so enter this route in the browser,
https://meetupservice.herokuapp.com/api/meetups/public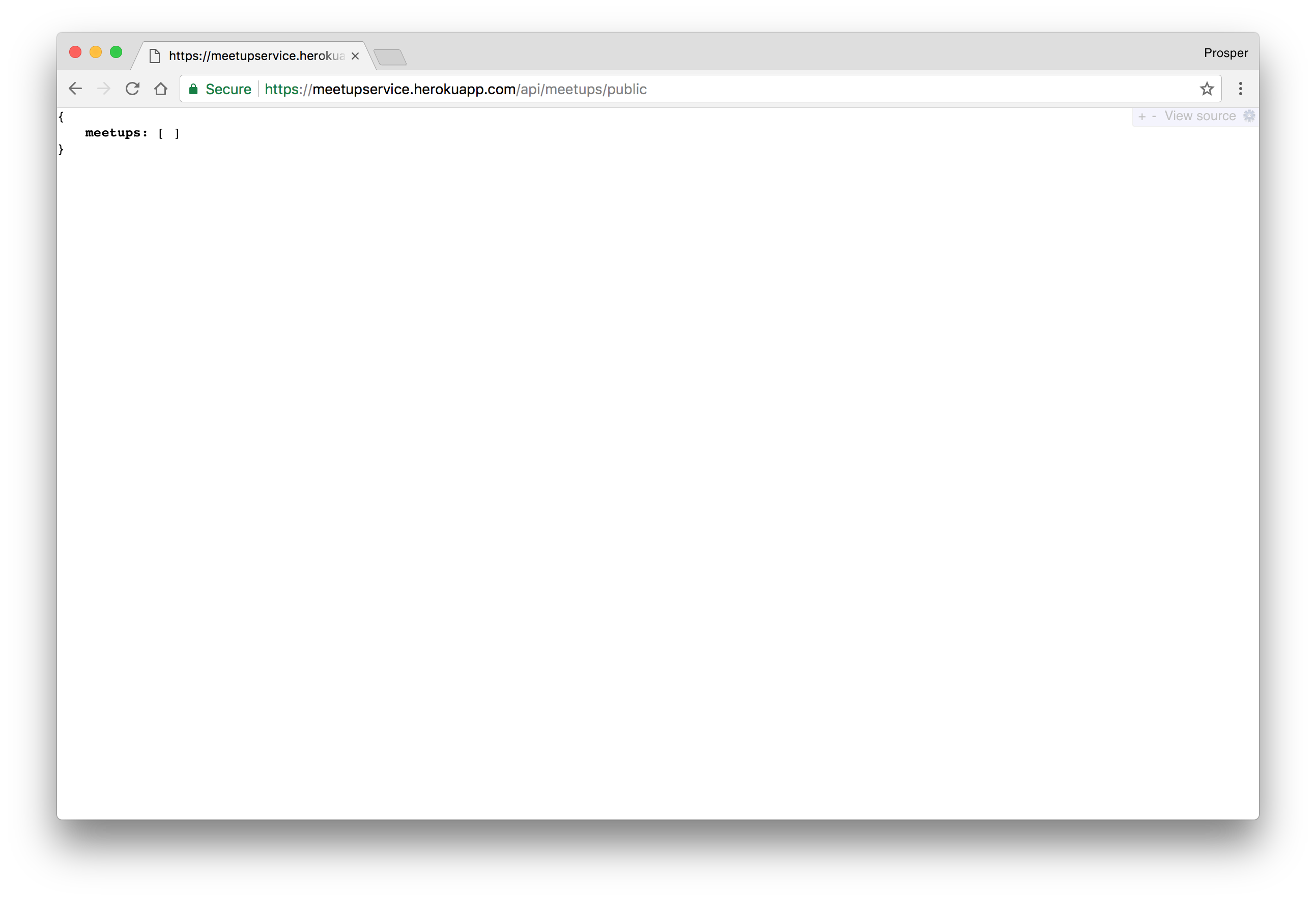
Let's make a POST request to the meetups API,
https://meetupservice.herokuapp.com/api/meetups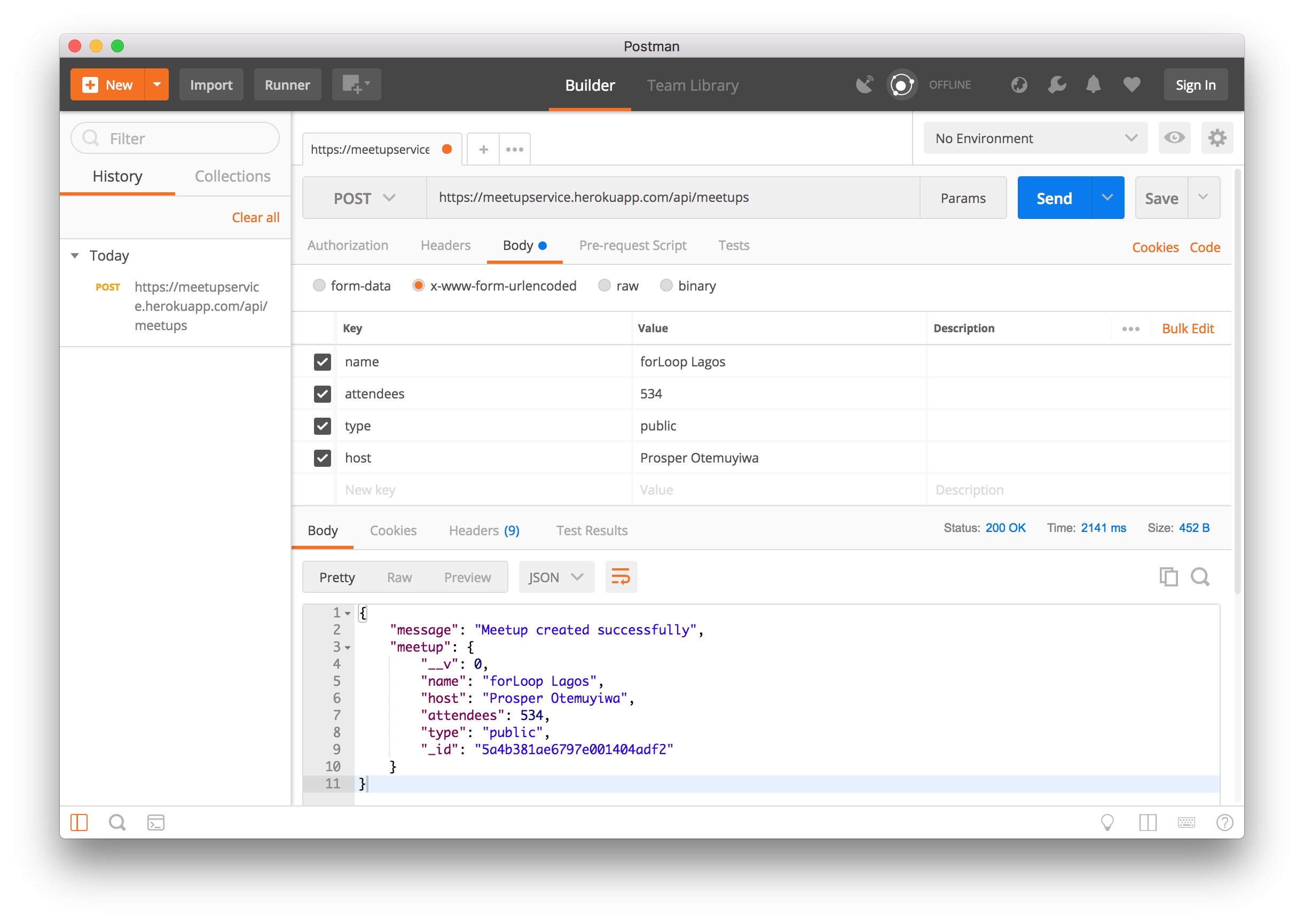
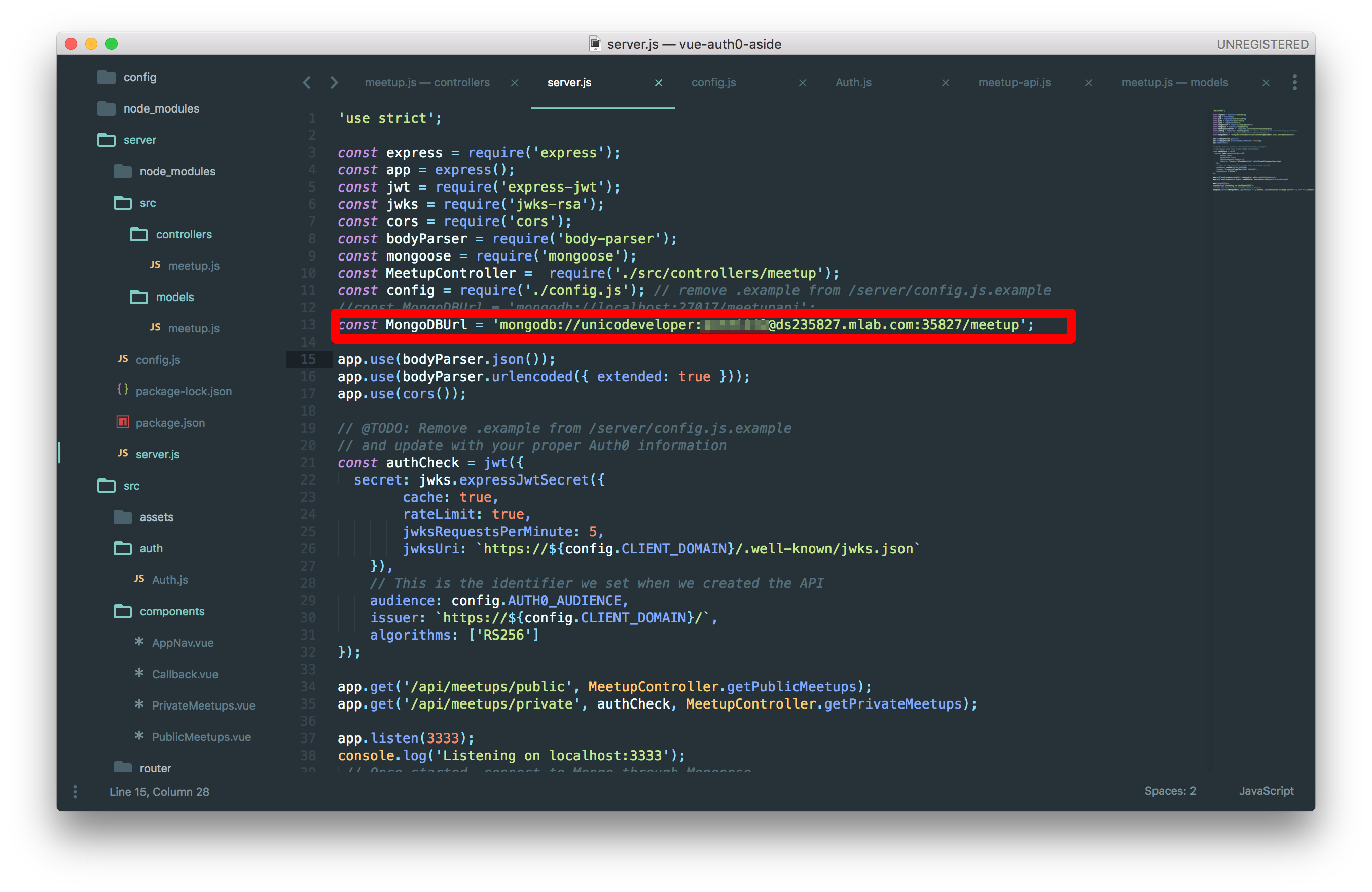
Note: I used the mLab's database that we deployed earlier.
Log in to mLab and check to see if the data exists.
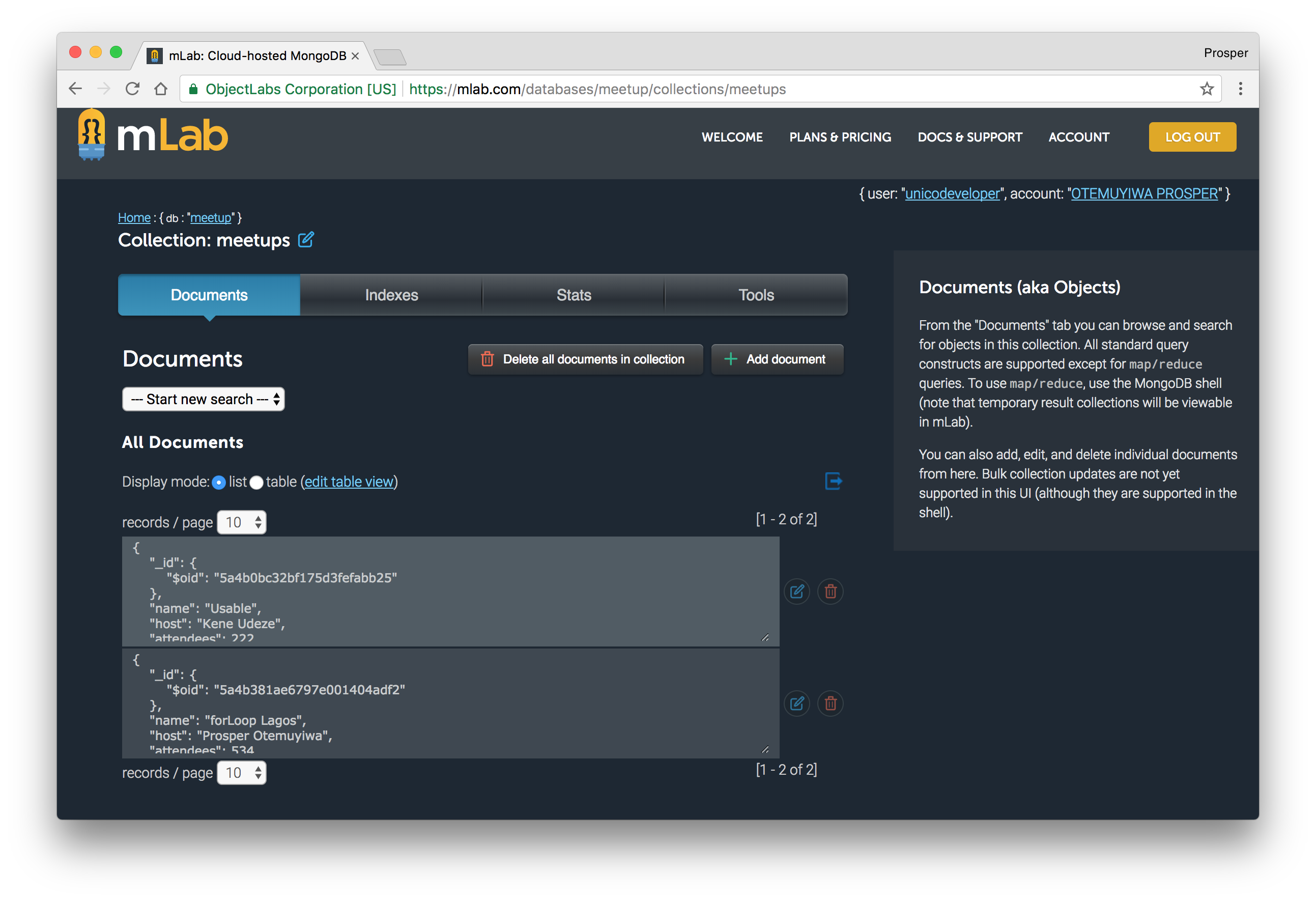
Make a Change
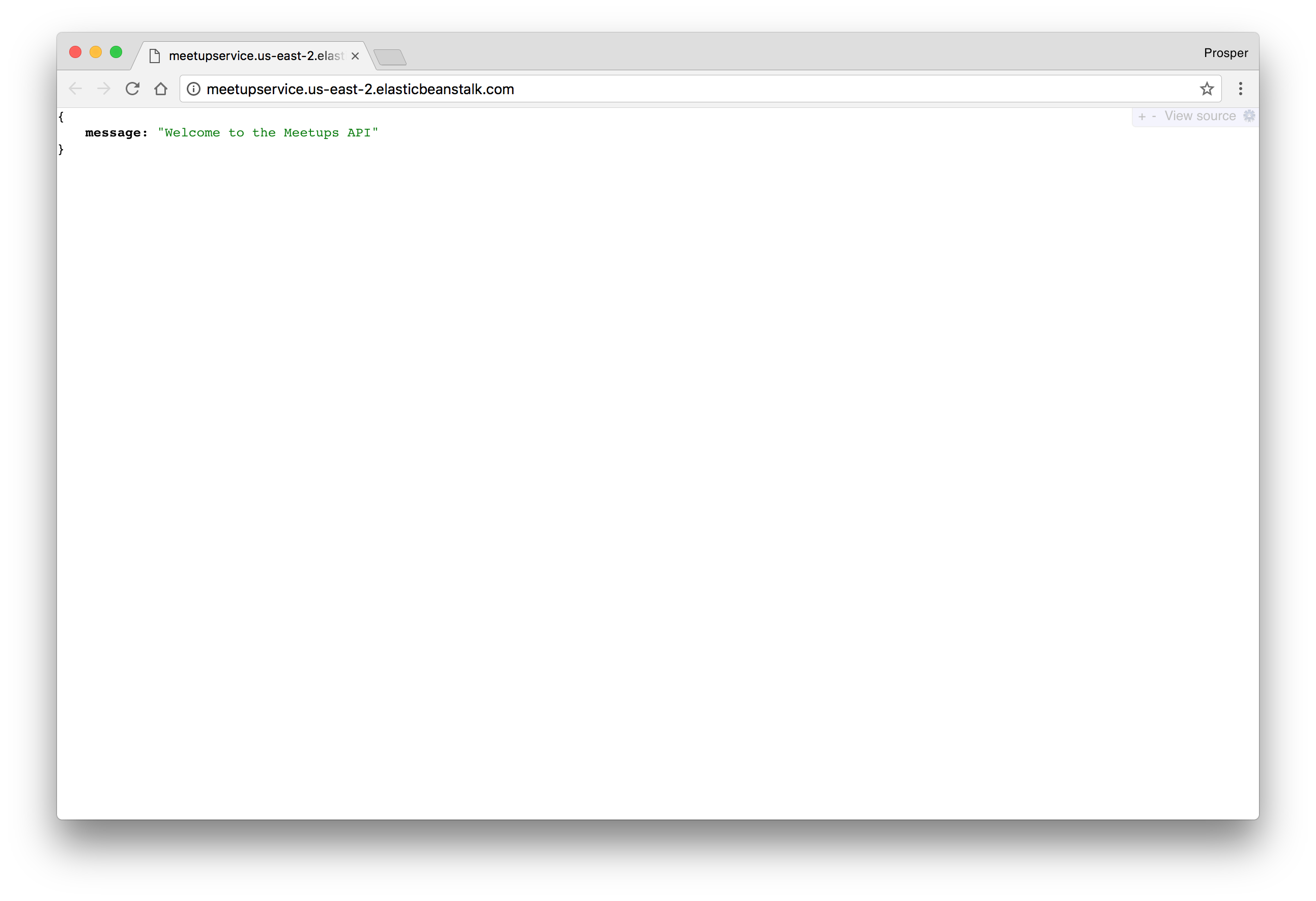
Let's make a little change to our app and see how effortlessly it deploys to production. Add a new route to the app.
Open
server.js... app.get('/', (req, res) => { return res.json({ message: "Welcome to the Meetups API" }); }); ...
Commit and push to your master branch. Now, go to the Activity tab of your Heroku Dashboard and notice the build. Reload your app and you'll see the difference.
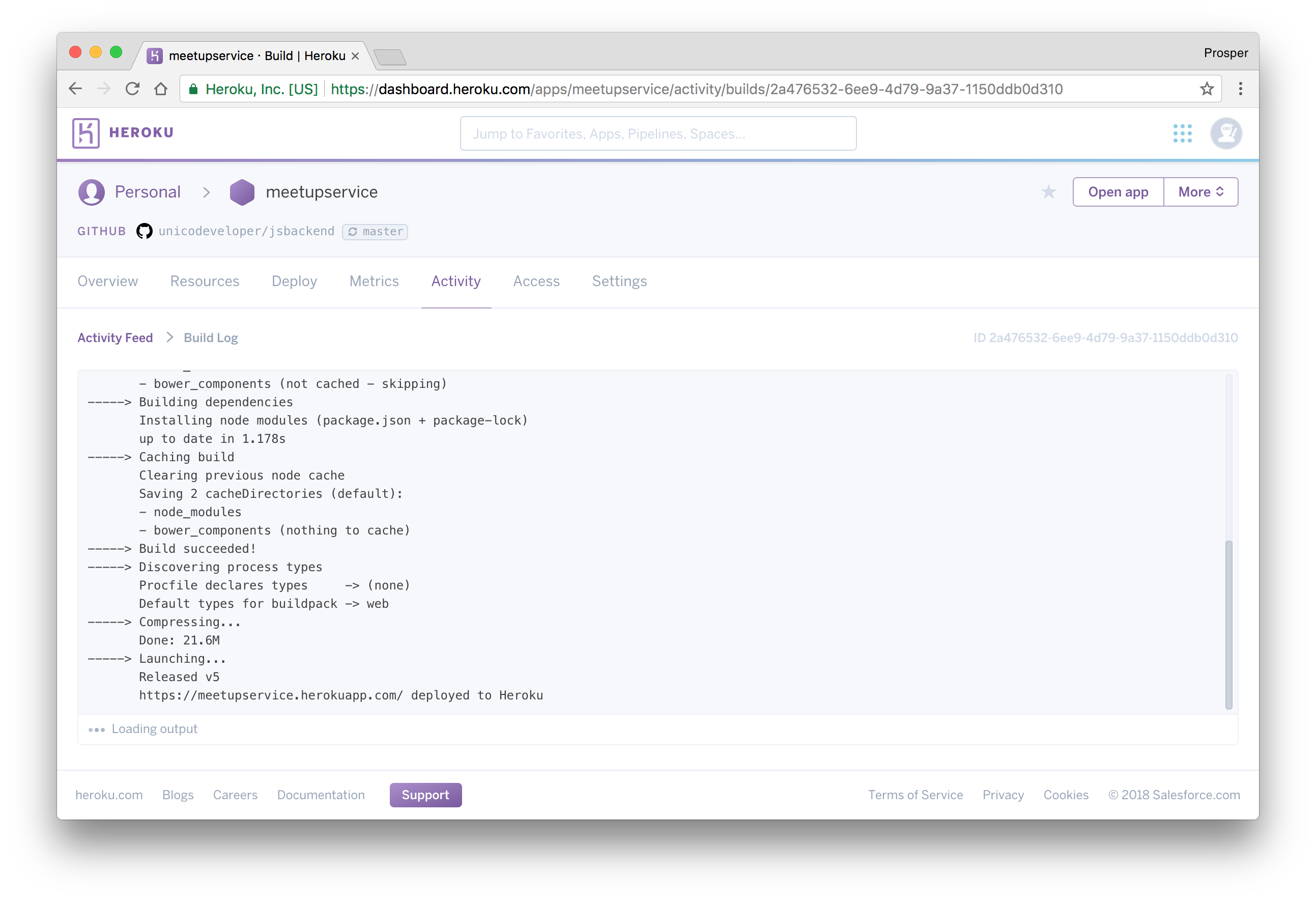
Caching & Cron Jobs
Heroku provides an array of addons for caching, from
memcache[fastly](https://www.fastly.com/)ironcacheFinally, you can use the Heroku Scheduler for running jobs on your app at scheduled time intervals.
Google Cloud
The Google Cloud platform is a trusted cloud platform that lots of companies and startups utilize in deploying and hosting their apps. The apps deployed on
Google CloudGoogle Cloud offers different options for hosting Node.js apps. The platform offers App Engine (Full managed), Compute Engine (Scalable VMs) and Container Engine (Kubernetes Clusters).
In our case, we'll use Google App Engine to deploy our Node.js backend. It abstracts the infrastructure away. Let's dive right in!
When using Google App Engine, you can choose the Standard or Flexible environment. The latter, like the name implies, allows you to install a lot of extensions and allows you to run deployment scripts using
package.jsonNote: You won't be charged without your permission.
Now, download the Google SDK and install the Google Cloud tools.
Initialize
gcloud
Go ahead and create an
app.yamlapp.yaml
runtime: nodejs env: flex manual_scaling: instances: 1 resources: cpu: 1 memory_gb: 0.5 disk_size_gb: 10
Configuration for the cloud servers are set in the
app.yamlIn your terminal, run the command below to set
the project IDgcloud config set project <projectID>
Now go ahead and run the following command to deploy the app:
gcloud app deploy
Our backend is finally live.
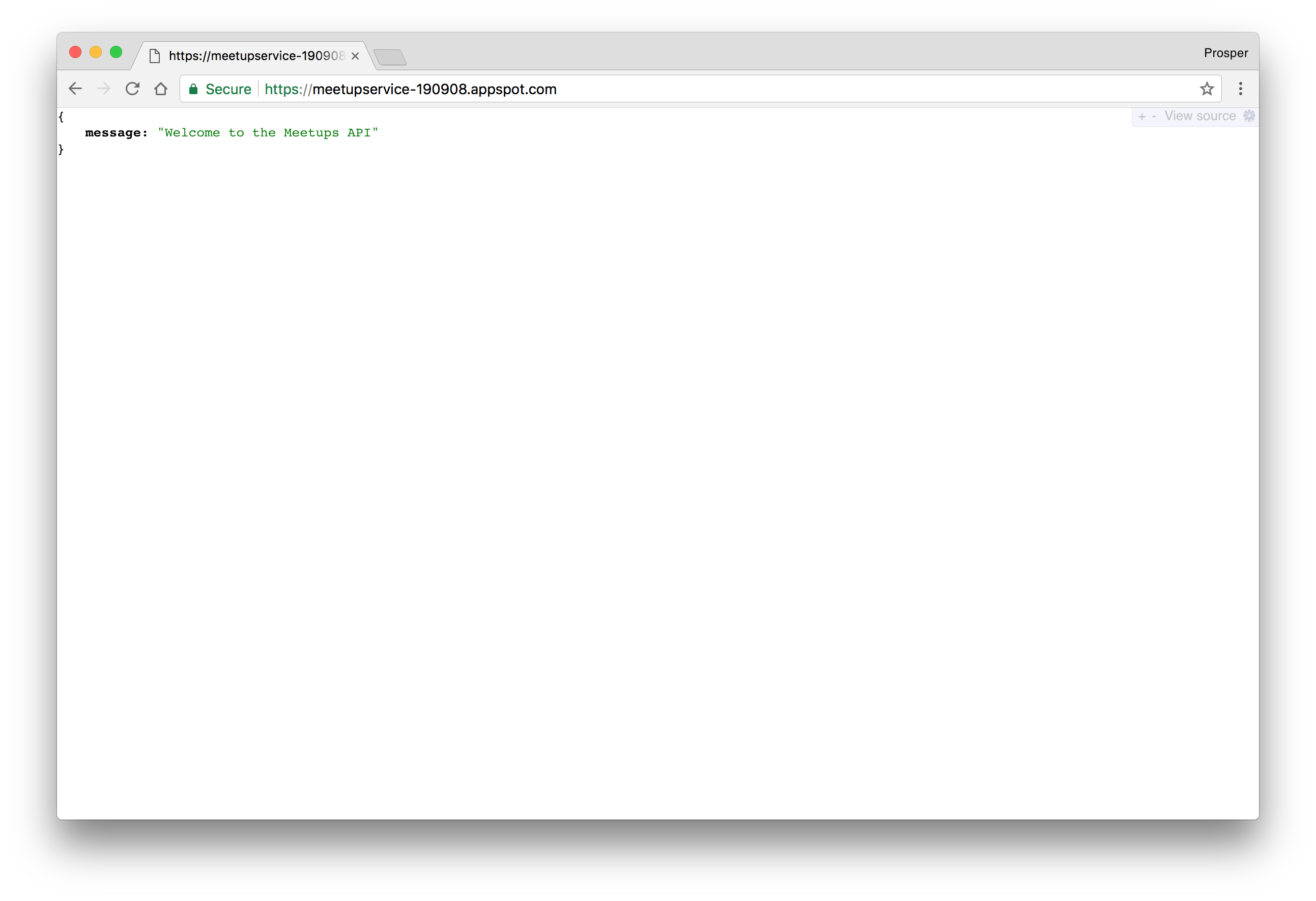
Caching & Cron Jobs
Google App Engine includes implementations of the standard Memcache and Memcached APIs. Check out how to use Redis Labs Memcache in your app on Google Cloud.
The App Engine Cron Service allows you to configure regularly scheduled tasks that operate at defined times or regular intervals. Check out how to schedule cron jobs for your Node.js apps on Google Cloud.
Now
Now is a tool that takes your JavaScript (Node.js) or Docker powered websites, applications and services to the cloud with ease, speed and reliability. Its deploy process is very simple. Any directory that contains a
package.jsonnow
Now offers the following:
- It serves apps over HTTP/2 protocol.
- It is not dependent on a single cloud provider.
- A
script can be defined in thebuild
file to allow a script to be run after the installation of the node modules.package.json - Oh, hosting static websites is a walk in the park too!
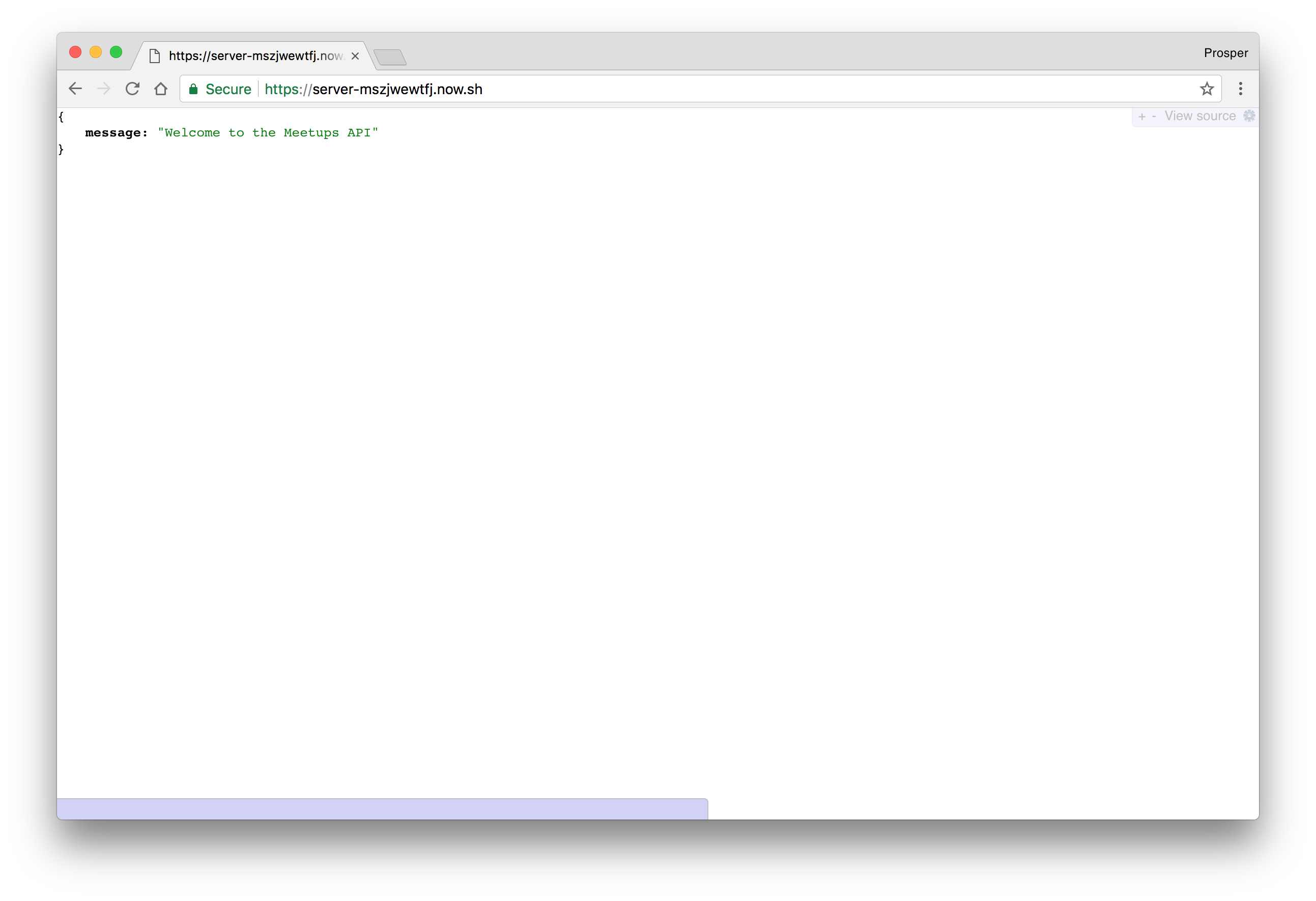
Deploying a Node.js app with Now involves the following:
- Download the Now Desktop or install the CLI via npm:
.npm install -g now - Switch to the project directory.
- Run the command
. There will be an authentication process.now
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is another massive cloud platform that allows you to scale your apps easily. Let's get started with deploying our Star Wars app on Azure.
With Microsoft Azure, you can deploy via:
- FTP.
- Syncing with a cloud folder.
- Local Git.
- Cloud based source control service such as GitHub or Bitbucket.
In our case, we'll set up deployment with Git.
- First, create an account with Microsoft Azure.
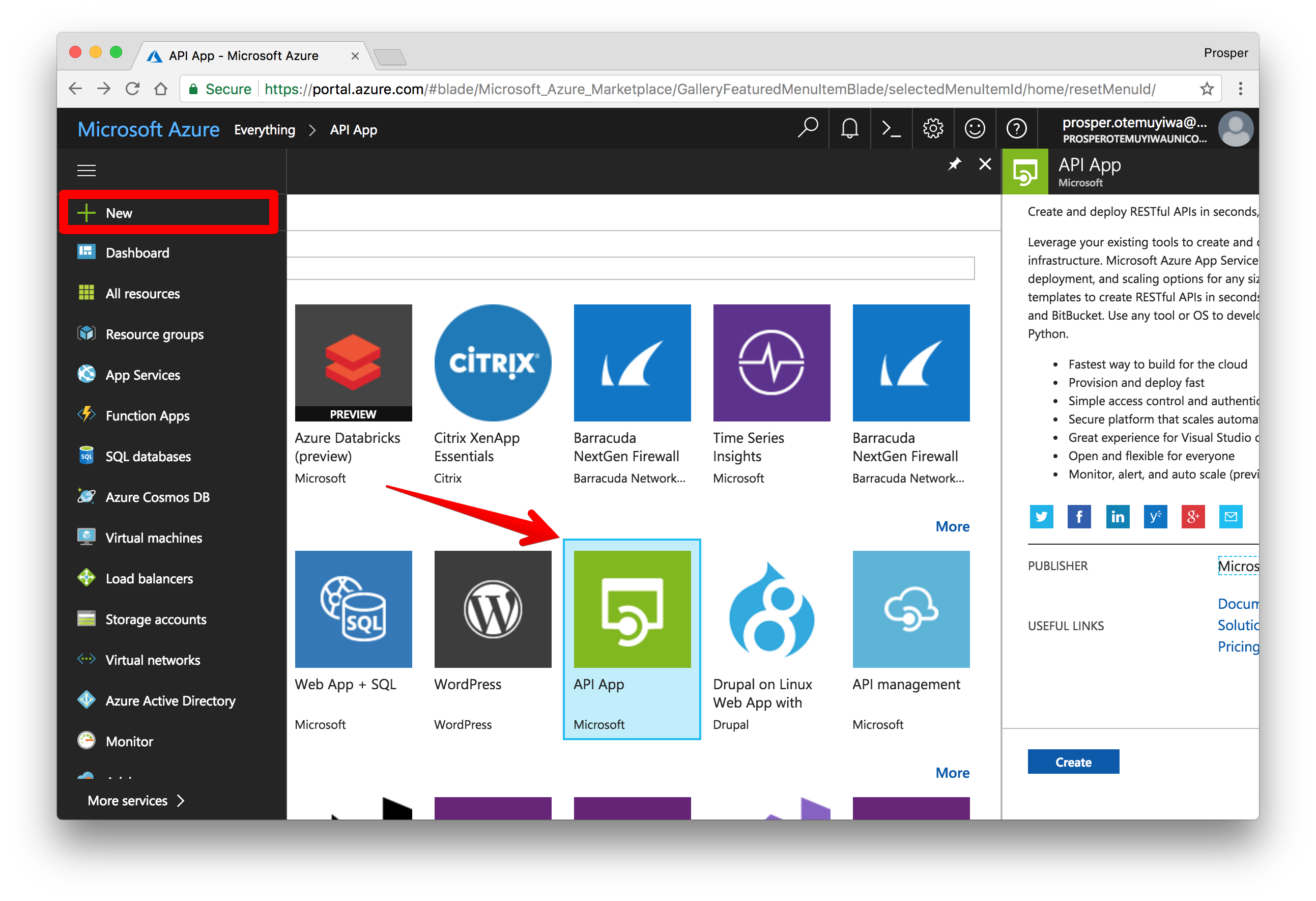
- Click on New on the left panel.
- Click See all just next to Marketplace.
Click API App, then go ahead and create.
- Select the type of subscription you are comfortable with.
- Give your name an app, and select a resource group.
- Now that our app has been created. Click on App Services by the left panel to see your app.
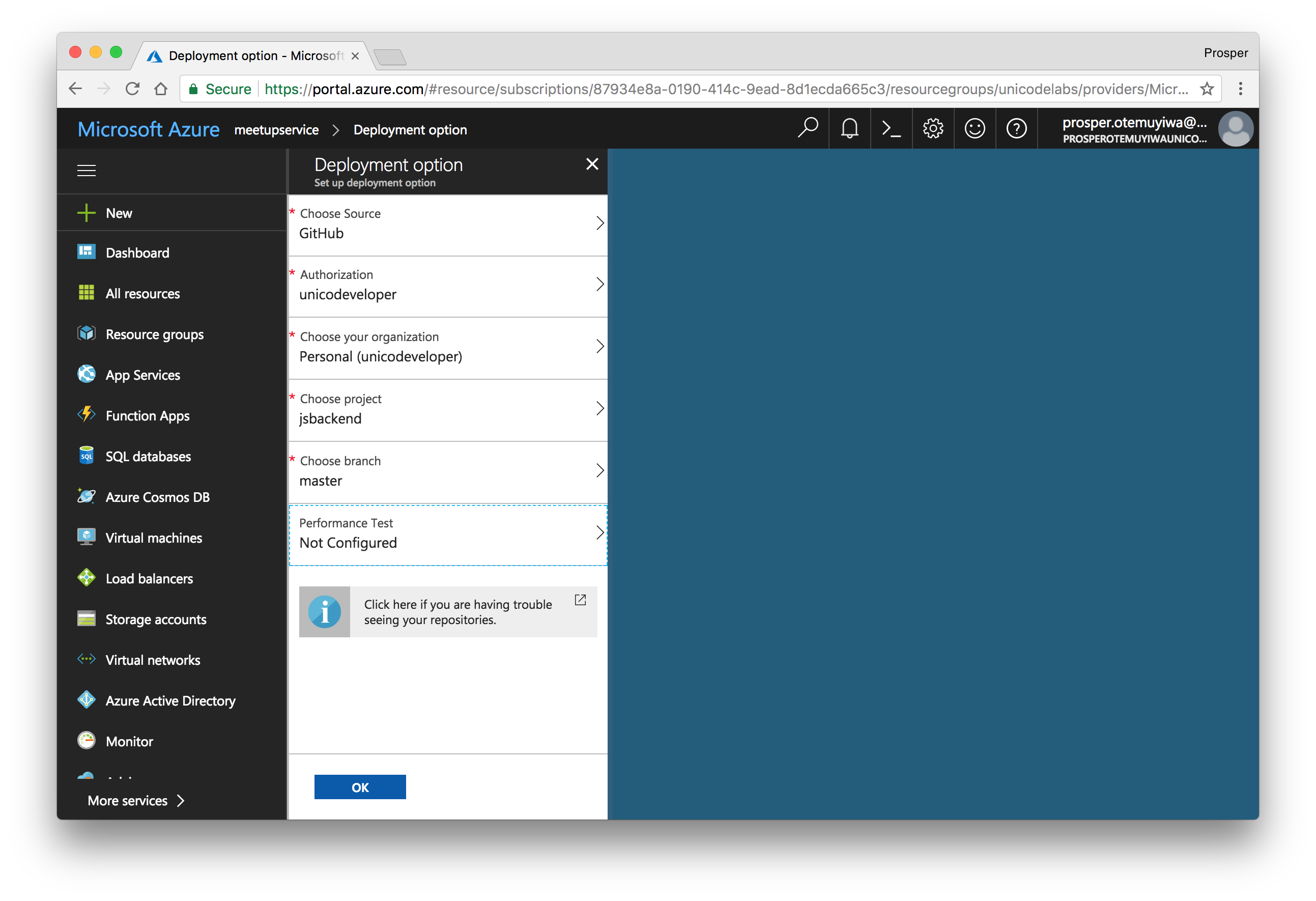
- Click on the app, choose Deployment options, then click on
.GitHub Authorize GitHub to access your repo. Choose the Project. Choose the branch.
Now browse to
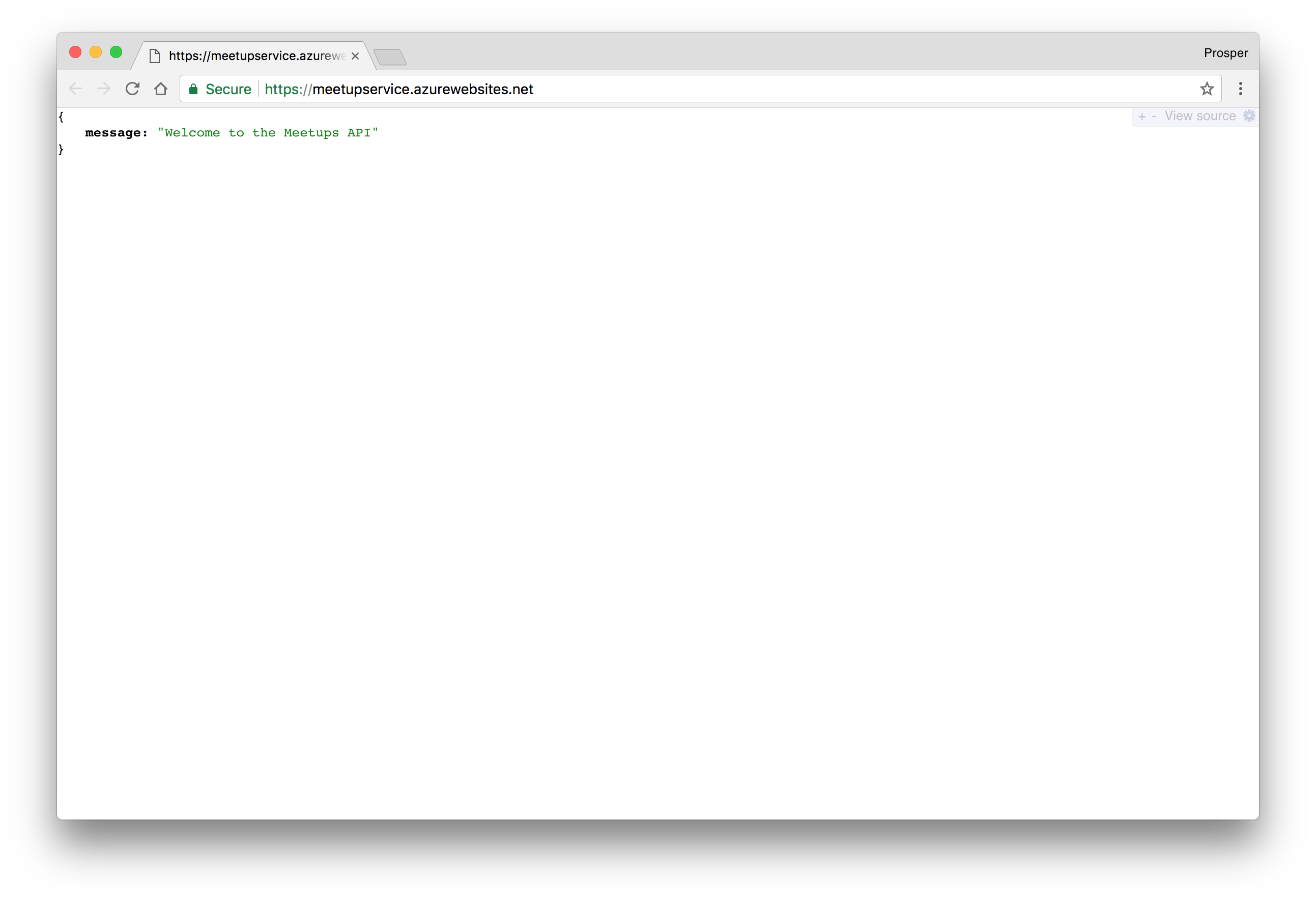
. In my case, it ishttp://[yoursitename].azurewebsites.net
.https://meetupservice.azurewebsites.net
Caching & Cron Jobs
Microsoft Azure offers Azure Redis Cache. It is based on the popular open source Redis cache. It's easy to create and use like so:
- Click New > Data + Storage > Redis Cache.
- Enter the name of the cache, select the region and create it.
Check out the documentation on how to use it.
For scheduling and running tasks, Azure offers a Scheduler. It allows you to:
- Call services inside or outside of Azure.
- Run jobs on any schedule.
- Use Azure Storage queues for long-running or offline jobs.
- Invoke Azure Service Bus queues.
Check out how to create and manage jobs using the Scheduler.
Amazon Web Services
More companies use AWS(Amazon Web Services) for storing all sorts of data ranging from images, mp3 files to videos than any other cloud platform. In fact, a lot of organizations like Uber, Spotify, Salesforce use Amazon Web Services wholly for hosting, deployment and infrastructure. AWS has a ton of developer products.
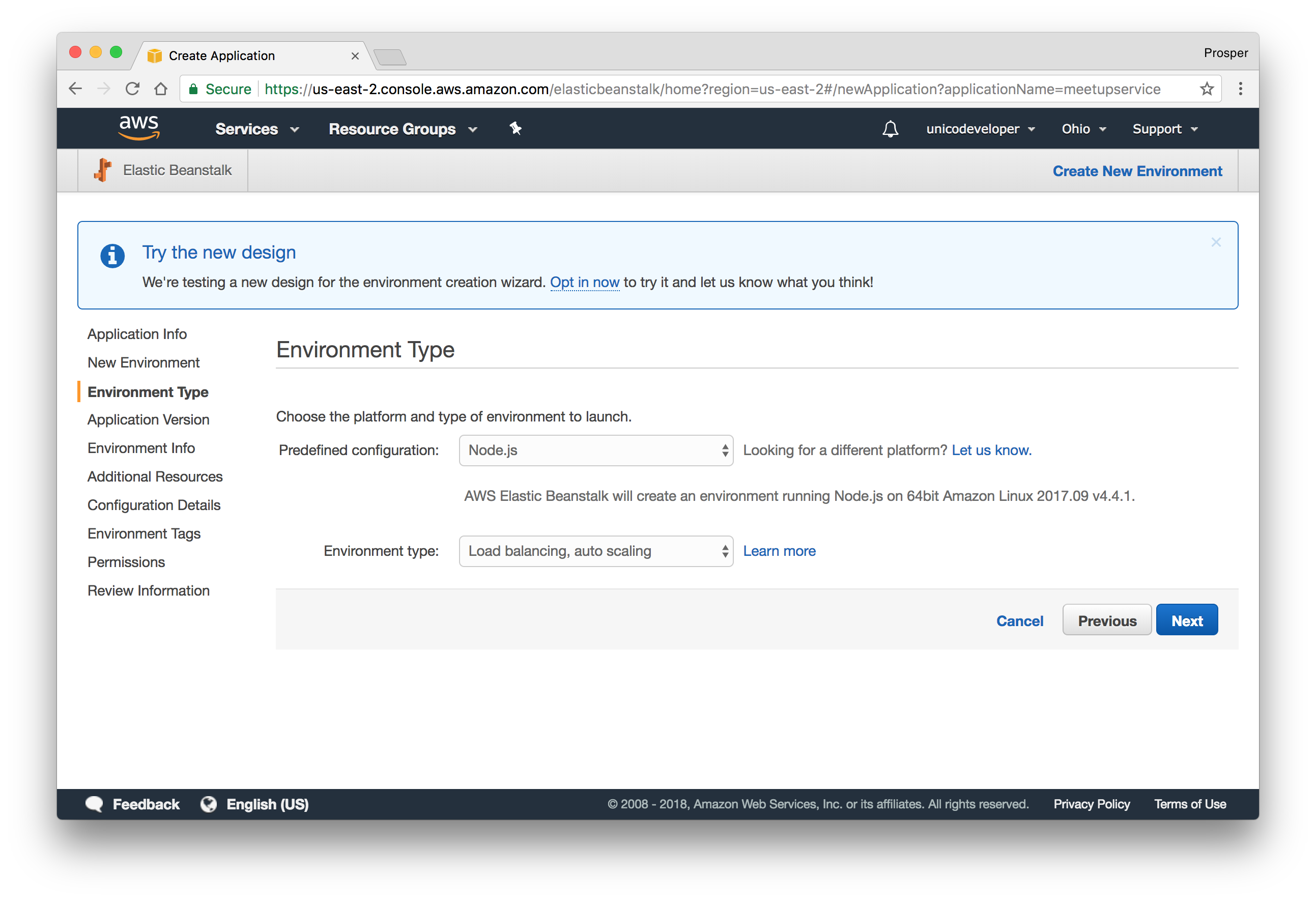
The service we'll use for deploying our backend Node.js app is Amazon Elastic Beanstalk. Let's get started.
- Sign up for an AWS account if you don't have one.
- Head over to Elastic Beanstalk console.
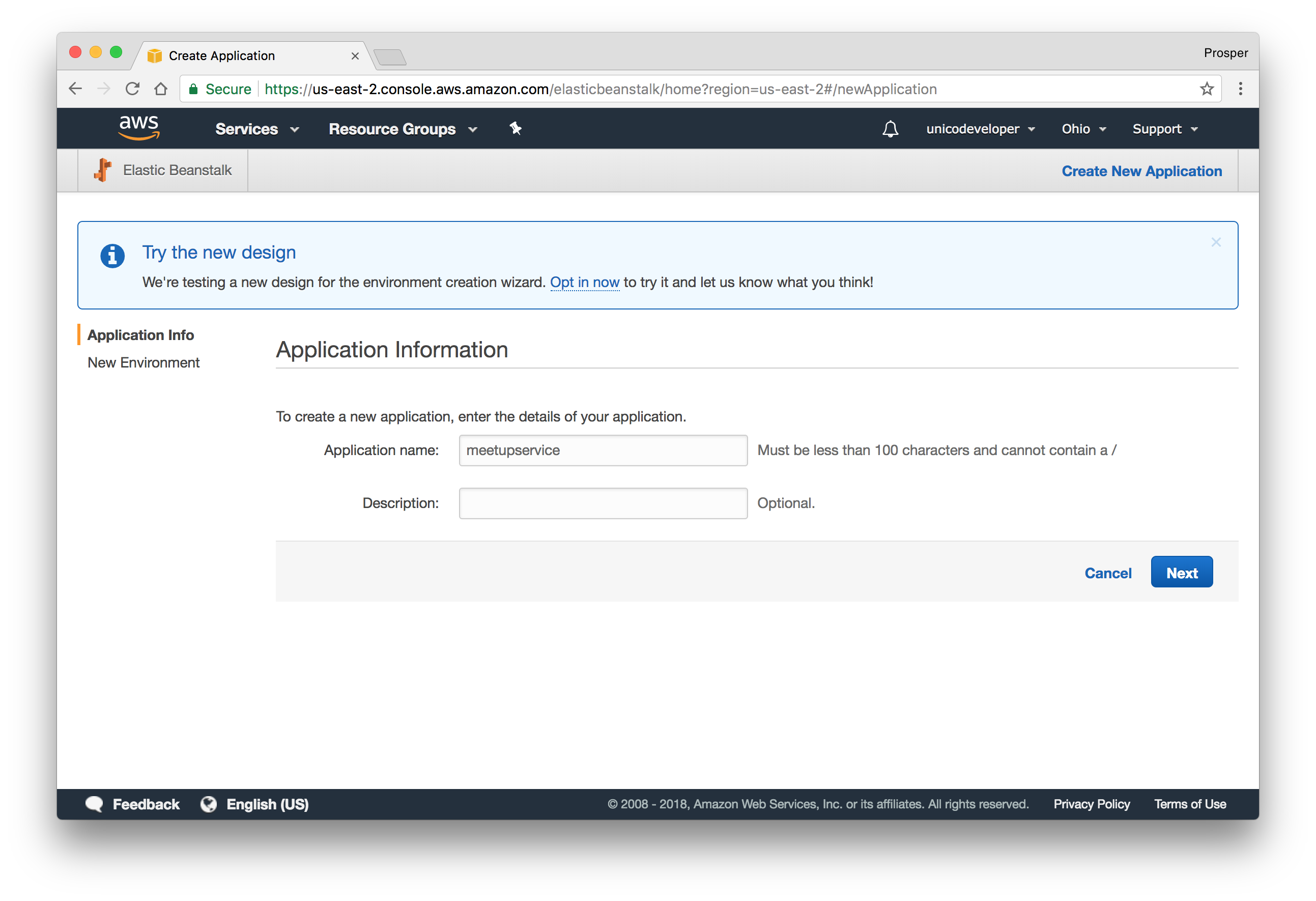
- Create a new app.
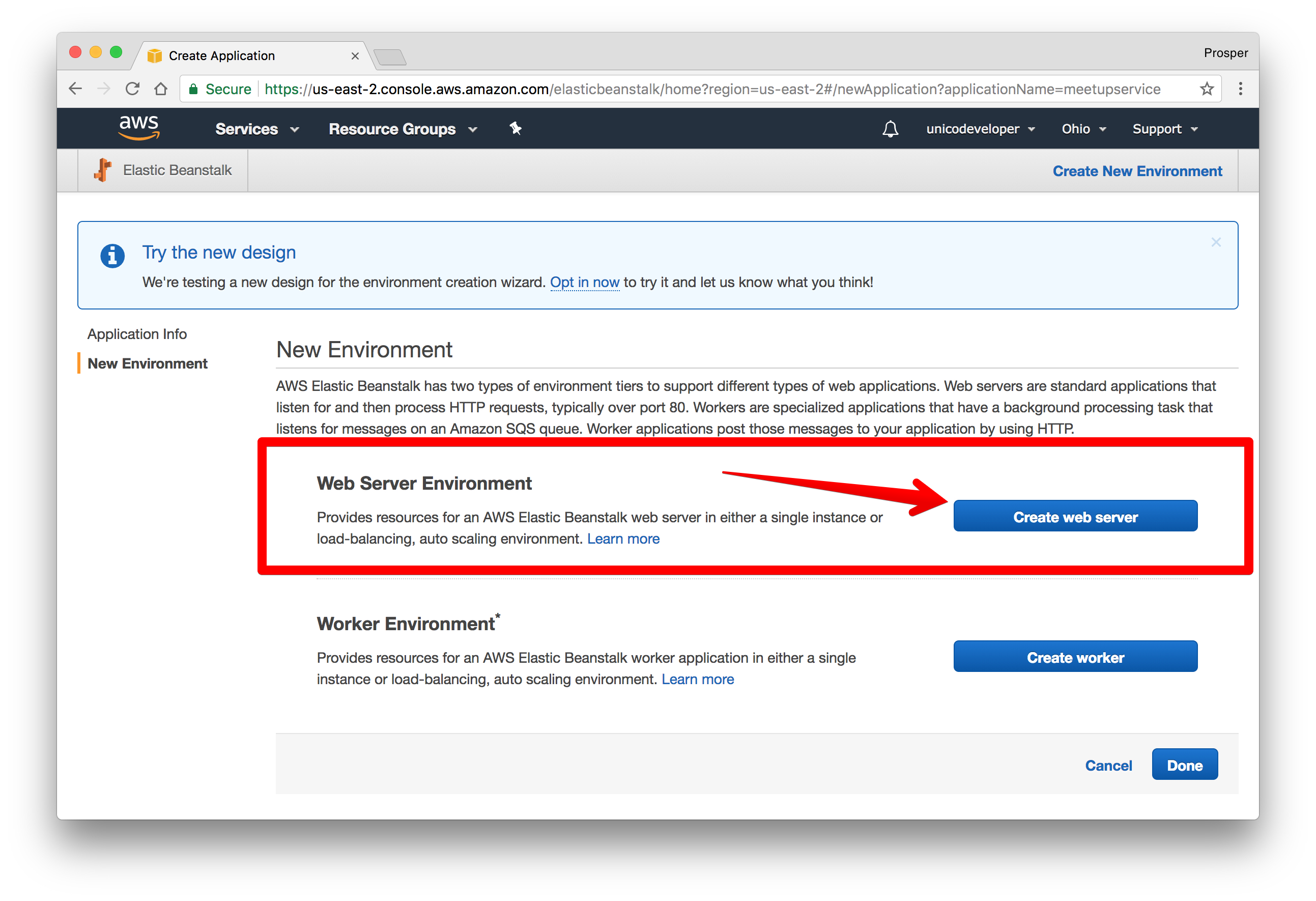
- Click on
.create web server - Create the web server environment.
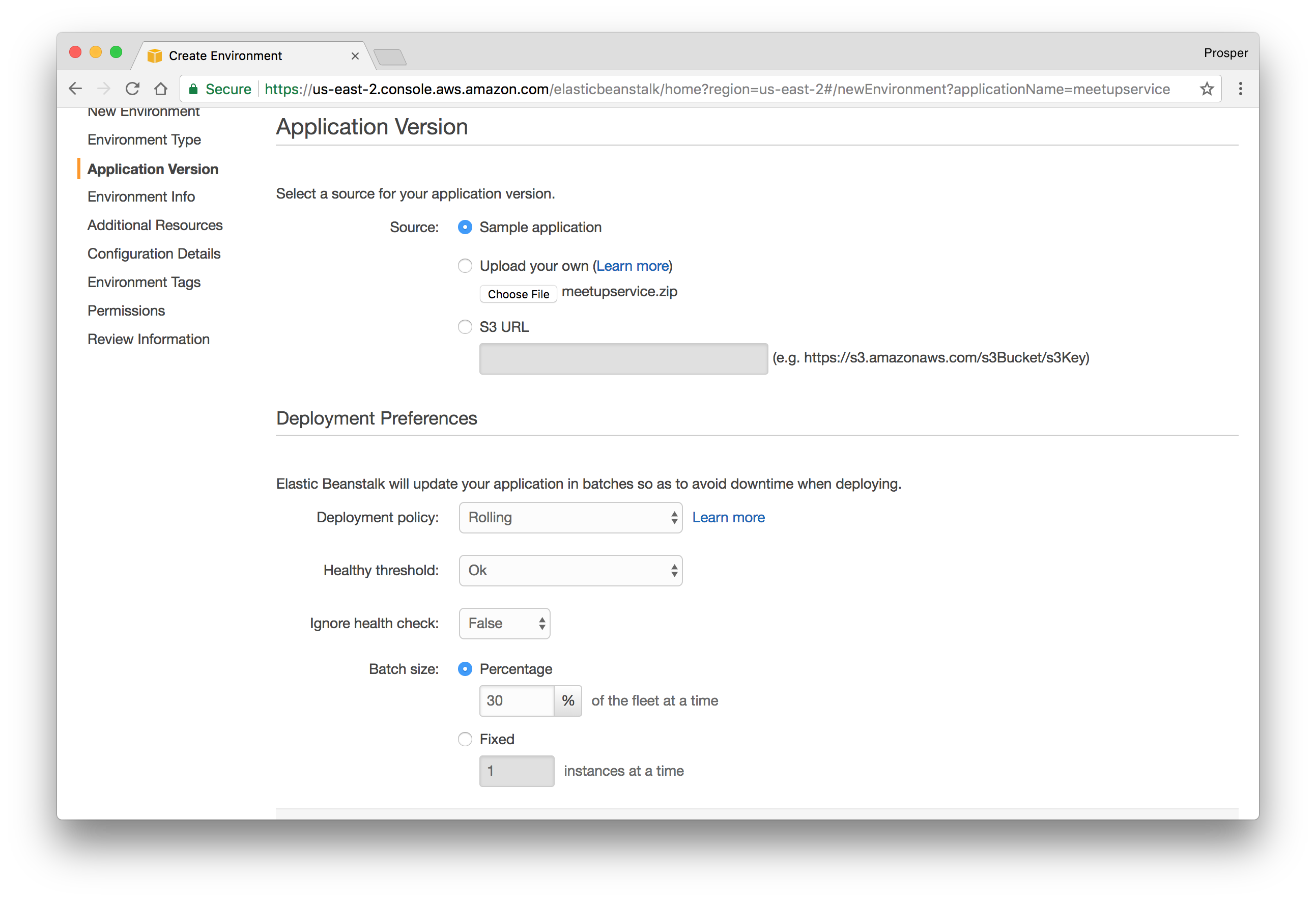
Upload your code. Elastic Beanstalk requires that you upload a zip file of your codebase. You can manually zip it up. But I prefer to do that from my terminal like so:
zip ../meetupservice.zip -r * .[^.]*- Now, upload it to AWS like so:
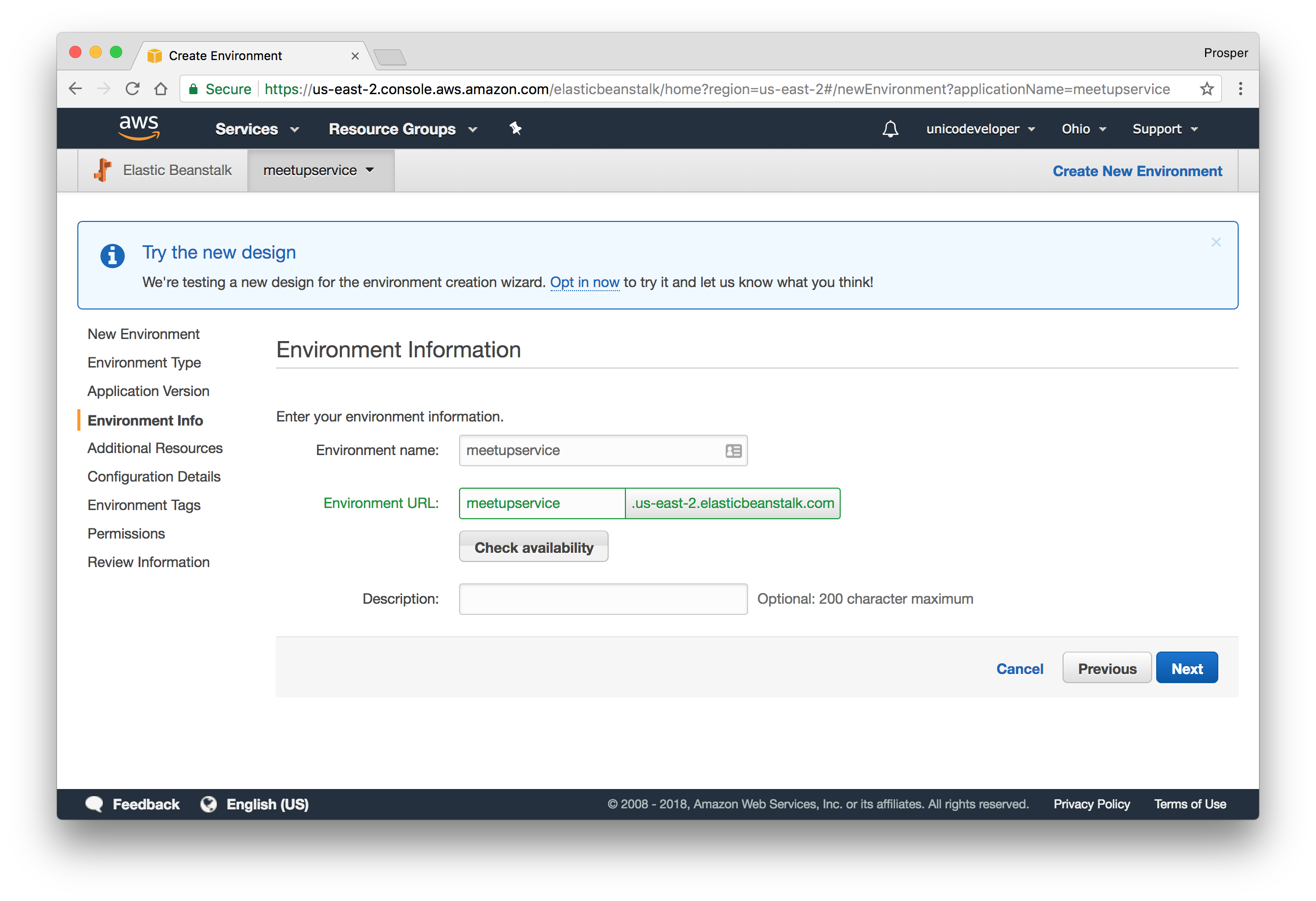
- Check availability for the app URL. Mine looks like this:
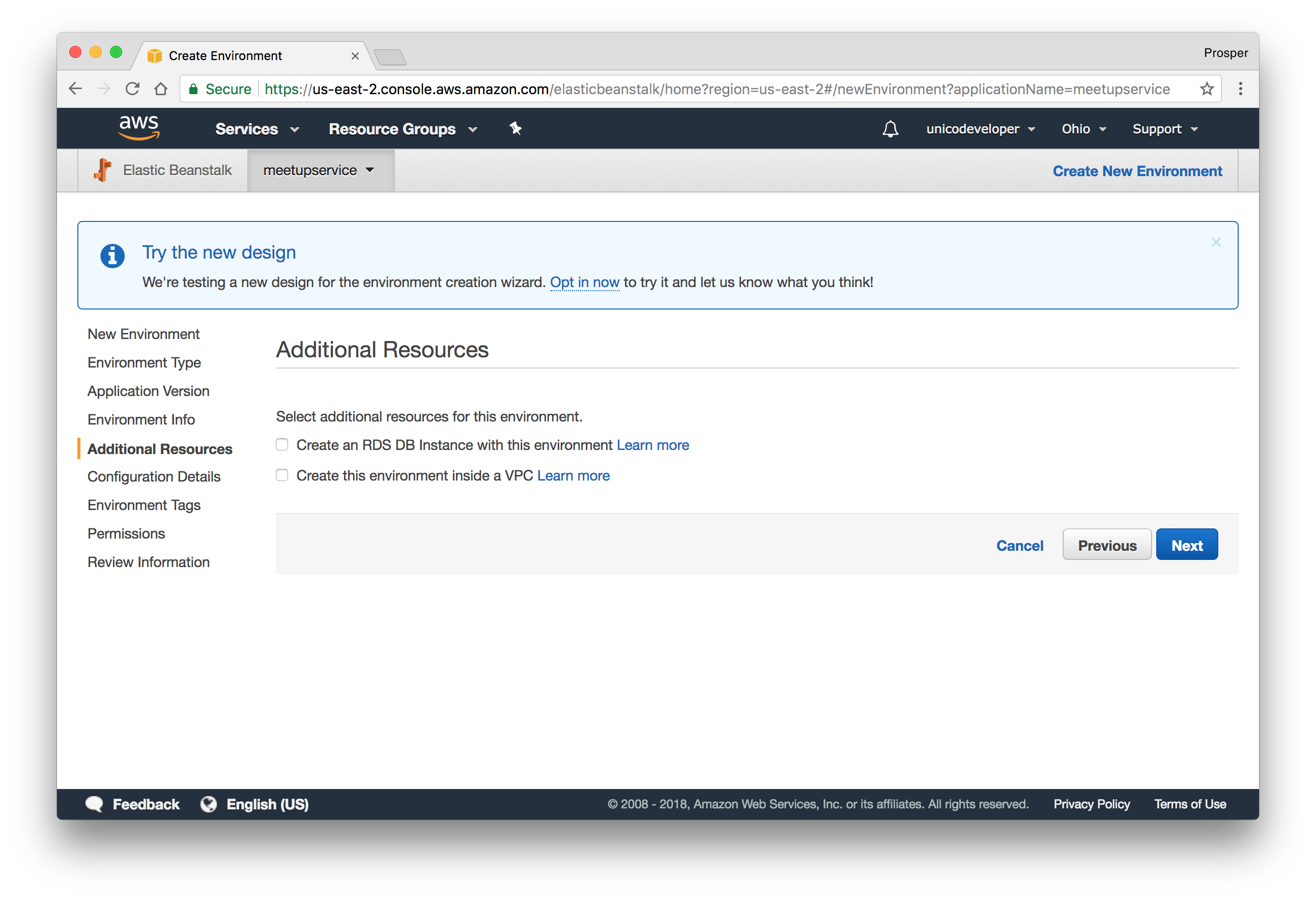
- The next page allows us to configure a Database Instance. Now our app already uses a remote MongoDB instance, so we can skip it.
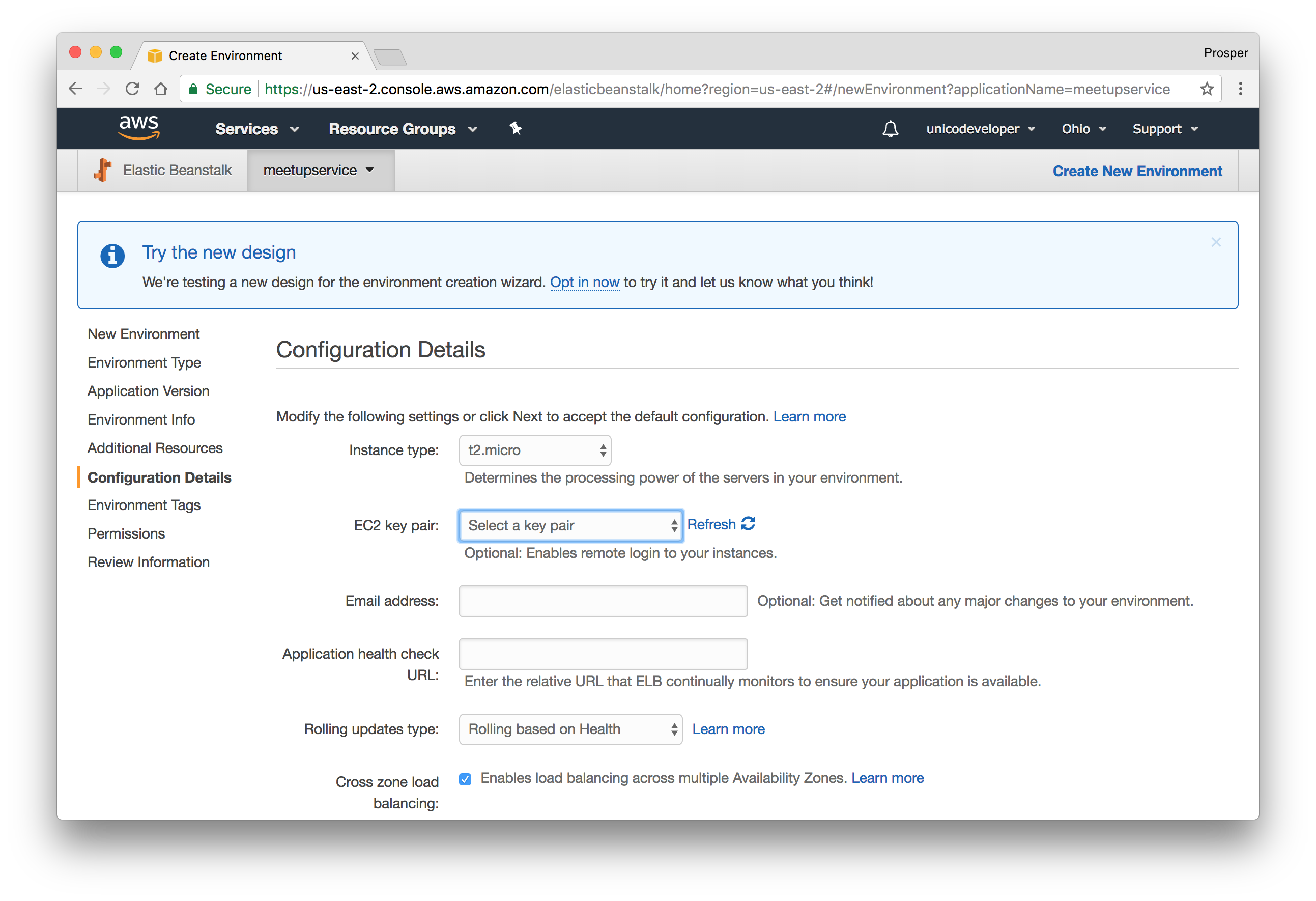
- This step allows us to modify our configuration details. The default one is okay for our app.
- The next step requires that we add any environment variables. Our app does not require one, so we'll skip this step.
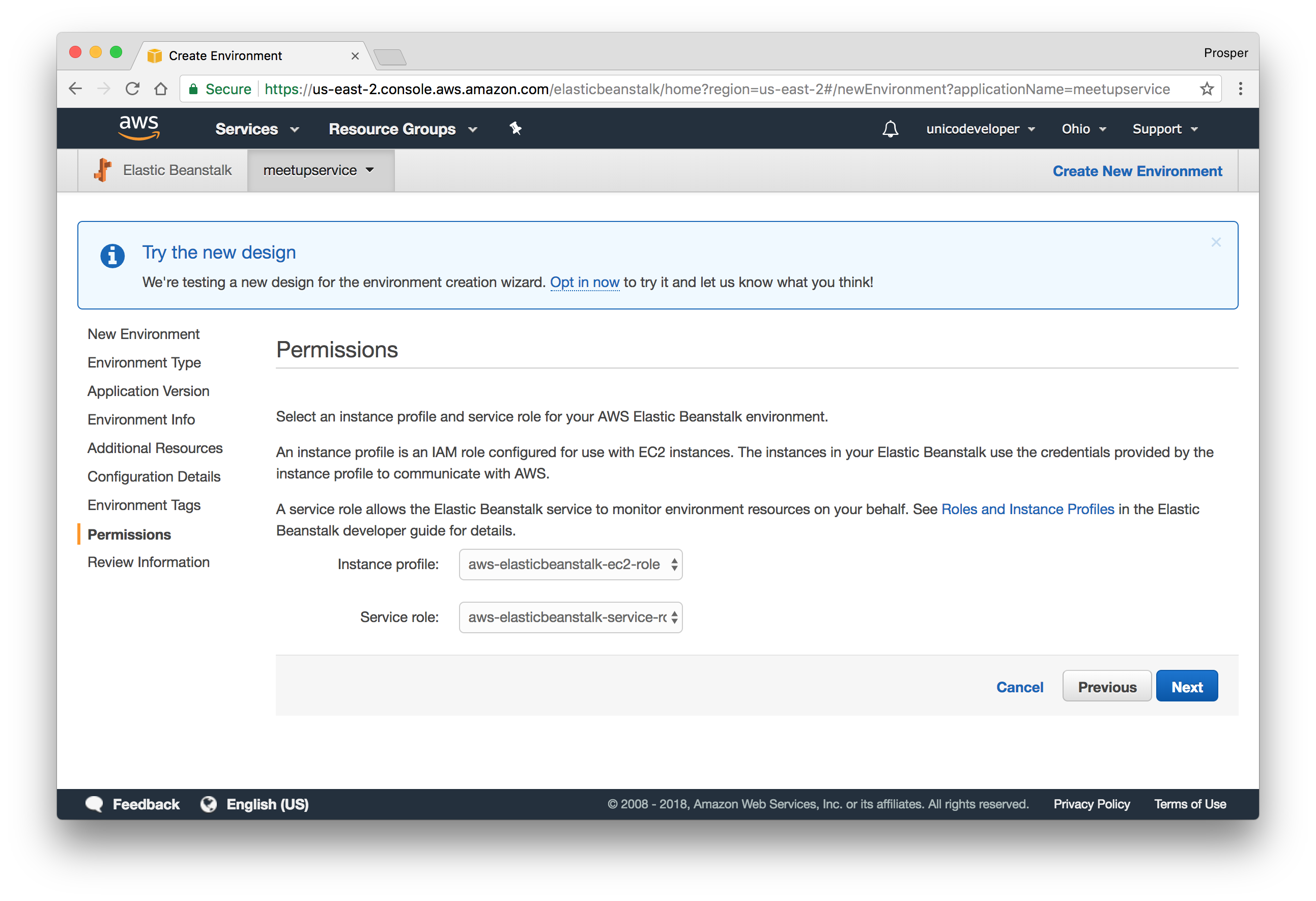
- Add Permission like so:
- Review the information before launching.
- Launch.
Caching and Cron Jobs
For caching, Amazon Web Services offers ElastiCache. It is a web service that makes it easy to deploy, operate, and scale an in-memory data store or cache in the cloud. Amazon ElastiCache supports two open-source in-memory engines:
- Redis.
- Memcached.
Amazon ElastiCache automatically detects and replaces failed nodes, reducing the overhead associated with self-managed infrastructures and provides a resilient system that mitigates the risk of overloaded databases, which slow website and application load times. Through integration with Amazon CloudWatch, Amazon ElastiCache provides enhanced visibility into key performance metrics associated with your Redis or Memcached nodes.
Companies like Airbnb, Healthguru, PlaceIQ and Tokyo Data Network use ElastiCache for caching at multiple layers spanning HTML fragments, results of expensive DB queries, ephemeral session data and search results.
You can set up a cron job on Elastic Beanstalk. Learn how to run cron jobs on Amazon Web Services(AWS) Elastic Beanstalk.
We have worked on a lot of database and code deployments. It's time for you to take a break!
Conclusion
There is no way we can cover all the different options available for deploying database and JavaScript backend/API applications or services. Here, we have covered deploying databases and Node.js backends to the cloud.
In the next post, we'll connect everything together by covering the deployment of JavaScript Single Page Applications and static websites. Stay tuned!
About Auth0
Auth0 by Okta takes a modern approach to customer identity and enables organizations to provide secure access to any application, for any user. Auth0 is a highly customizable platform that is as simple as development teams want, and as flexible as they need. Safeguarding billions of login transactions each month, Auth0 delivers convenience, privacy, and security so customers can focus on innovation. For more information, visit https://auth0.com.
About the author

Prosper Otemuyiwa
Former Auth0 Employee (Auth0 Alumni)